Fig. 2.
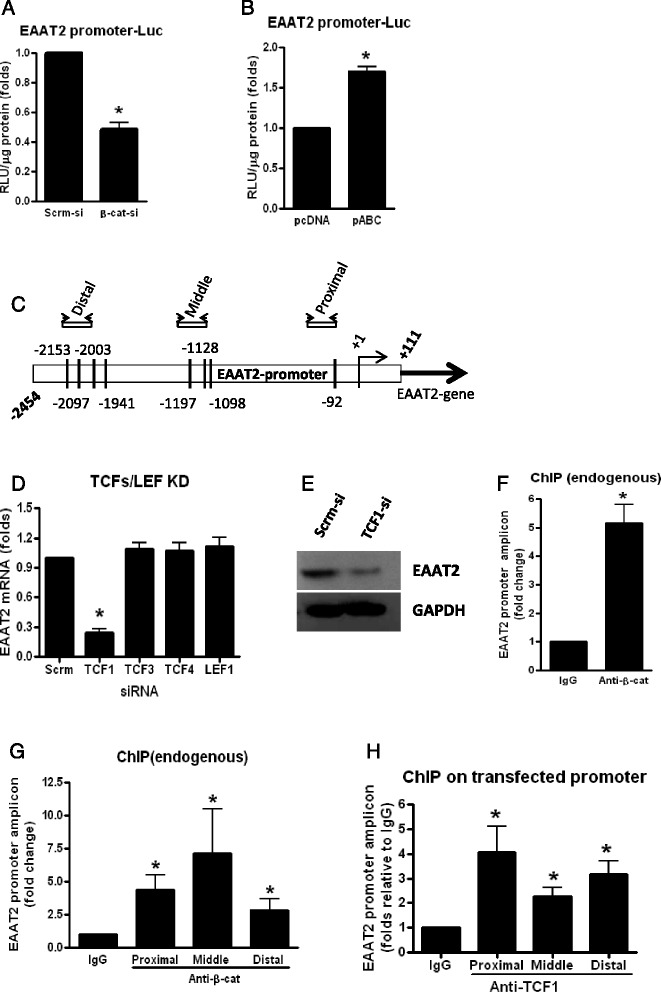
β-Catenin partners with TCF-1 to positively regulate EAAT2 at the level of transcription in PDAs. PDAs were transfected with β-catenin siRNA or Scrm-Si, and 48 h post transfection, cells were transfected with an EAAT2 promoter linked to luciferase, and 24 h later, luciferase activity was measured (a). b PDAs were transfected with pABC or pcDNA, and 24 h post transfection, cells were transfected with EAAT2 promoter linked to luciferase, and 24 h later, luciferase activity was measured. c Identification of putative TCF/LEF binding sites on the EAAT2 promoter. Shown in c is a ~2.5-kb promoter of EAAT2 illustrating TCF/LEF binding sites present in clusters and the regions selected for designing primers for real-time PCR. PDAs were transfected with siRNAs to knockdown TCF-1, TCF-3, TCF-4, LEF1, or scrambled siRNA (d, e), and 72 h post transfection, real-time qPCR was performed to measure the levels of EAAT2 mRNA (d) and protein by WB (e). PDAs (~2 × 106 cells) were cross-linked with 1.0 % formaldehyde and sonicated to generate chromatin preparations (f–h). ChIP was performed using antibodies against β-catenin (f, g) or TCF-1 (h) (5 μg antibody/IP). PDAs were transfected with EAAT2-prom, and 24 h later, ChIP was run (h). Data shown are normalized to a nontargeting IgG control and reported as a fold change relative to IgG. Asterisks indicate a p < 0.05 relative to the respective control using Student’s t test. Error bars indicate SD
