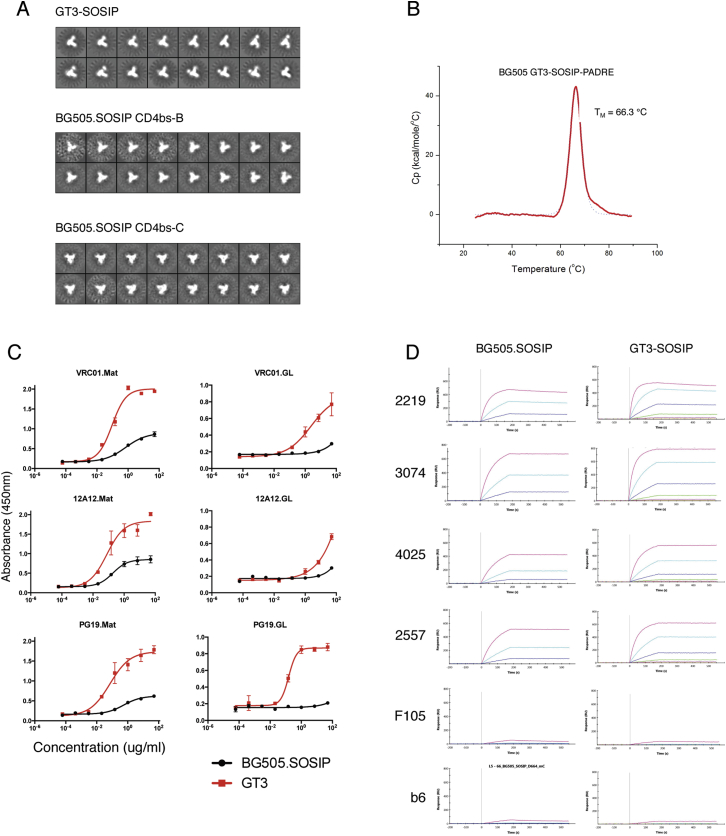
Figure S3.
Characterization and Structural Analysis of BG505 GT3.1 SOSIP and ABC SOSIP Trimers, Related to Figure 1
(A) Negative-stain 2D class average images of the GT3.1 SOSIP, CD4bs-B SOSIP and CD4bs-C SOSIP are shown. 37% of GT3.1 SOSIP trimers were classified as closed native-like trimers, 63% as open native-like trimers and 0% as non-native-like trimers.
(B) DSC thermogram of GT3.1 SOSIP.
(C) ELISA analysis of mature and GLRev VRC01-class Ab binding to BG505 SOSIP and BG505 GT3.1 SOSIP.
(D) SPR sensograms of BG505 SOSIP and BG505 GT3.1 SOSIP as analytes and non-nAbs IgGs as ligands. Maximum analyte concentrations were 990 nM and 1.3 uM for BG505 SOSIP and BG505 GT3 SOSIP, respectively, and lower concentrations teseted were 4-fold dilutions.