Fig. 5. Dependence of spinal and/or peripheral nicotine anti-allodynia on α6.
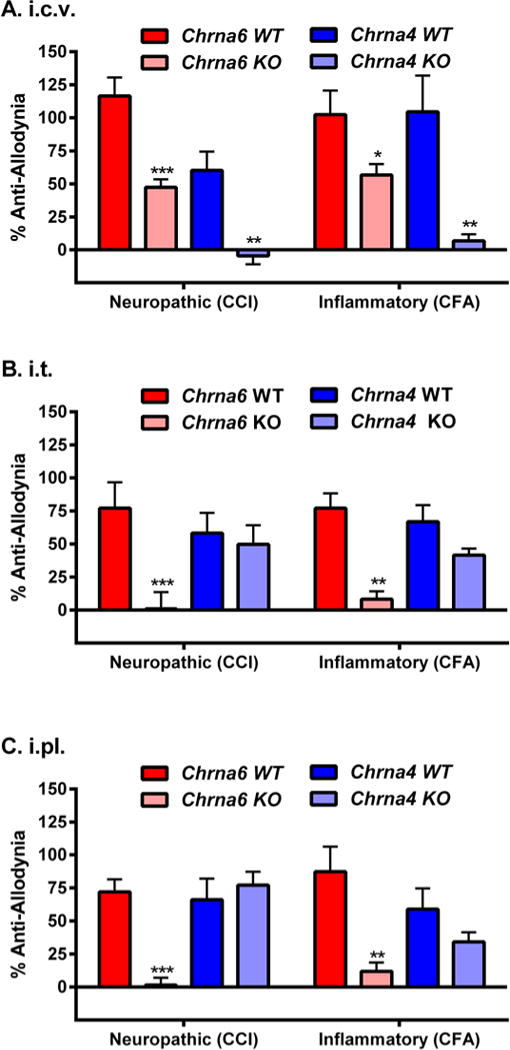
A head-to-head comparison of supraspinal (25 μg, i.c.v.; graph A), spinal (17 μg, i.t.; graph B) and peripheral (50 μg, i.pl.; graph C) nicotine anti-allodynia against neuropathic (CCI) and inflammatory (CFA) pain in Chrna6 (α6*) and Chrna4 (α4*) WT and KO mice tested using identical parameters at the peak of allodynia (14 days post-CCI, 3 days post-CFA). Bars (n=5–6 mice/genotype/injury) represent mean ± SEM percentage of maximum possible anti-allodynia (see Materials and Methods). **P<0.01, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared to analogous WT.
