Fig. 7. Modulation of P2X2/3 agonist-induced pain and hypersensitivity by nicotine in Chrna6 mutant mice.
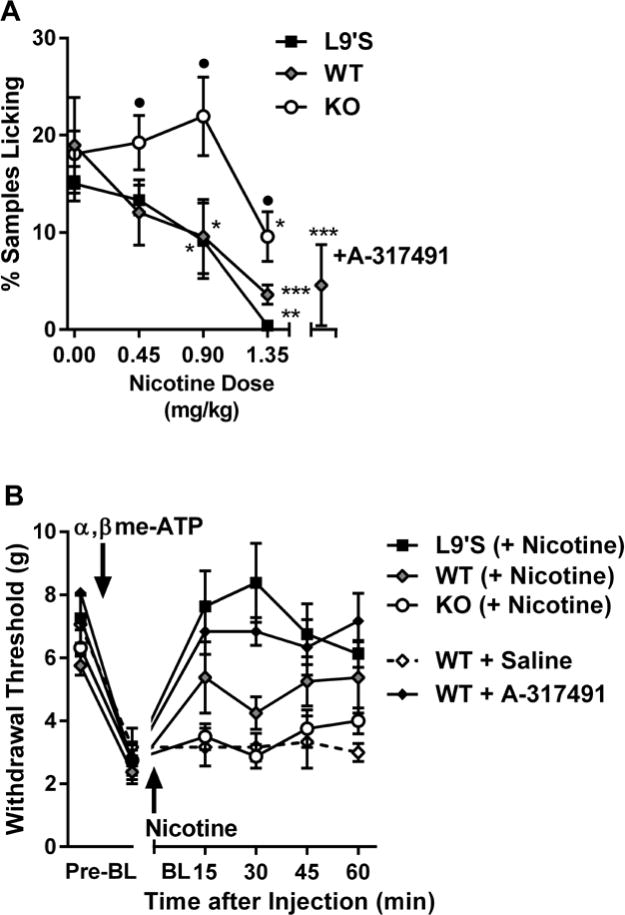
(A) Intrathecal administration of α,βme-ATP produces nocifensive (licking) behavior inhibited by the P2X3 antagonist, A-317491 (300 nmol, intraplantar), and systemic nicotine in WT and L9’S but not KO mice. Symbols (n=4–11 mice/dose/genotype) represent mean ± SEM samples featuring licking behavior (see Materials and Methods). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared to 0 dose within genotype. •P<0.05 compared to other genotypes within dose. (B) Intrathecal administration of α,βme-ATP produces mechanical allodynia reversed by A-317491 (300 nmol, intraplantar) and nicotine (0.9 mg/kg) in WT and L9’S but not KO mice. Symbols (n=4 mice/genotype or drug) represent mean ± SEM paw withdrawal threshold at each time point.
