Table 1.
Chemical strategies and principles applied to the discovery of antagonists for cavity insertion methyllysine binders and surface groove methyllysine binders.
| Cavity Insertion Binders | Surface Groove Binders | |
|---|---|---|
| Hit Discovery & Screening Strategies | Screen focused small molecule or fragment libraries Employ target class cross screening Utilize structure-based design for hit optimization |
Apply structure-based design Screen peptide or peptoid libraries |
| Design Principles | Exploit cation-π and H-bonding interactions in aromatic cage Utilize conformational constrained alkyl amines |
Use available Kme peptide SAR Target binding sites adjacent to aromatic cage Introduce unnatural amino acids, Kme mimics, and non-peptidic features |
| Major Challenge | Fragment-like size may result in low affinity | Low cell permeability may decrease overall utility |
| Example | L3MBTL1 + H4K20me2 (pdb 2PQW)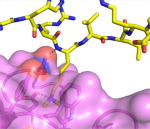
|
CBX7 + H3K27me3 (pdb 4X3K)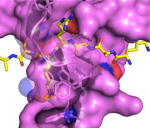
|
