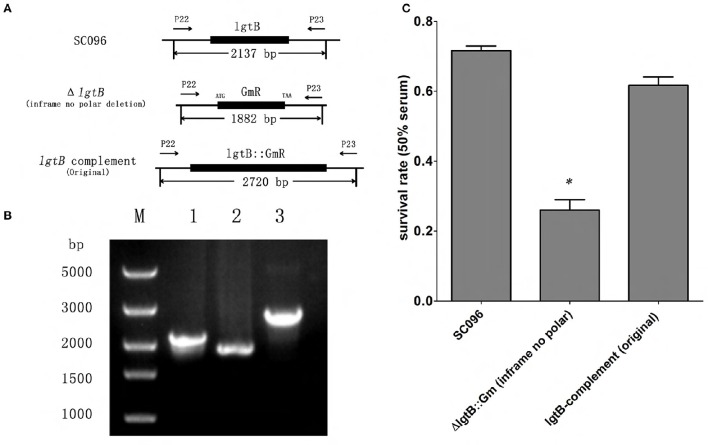
Figure 5.
Construction and verification of lgtB in-frame non polar mutant and the original complemented strain. (A) Schematic of lgtB in-frame non polar mutant and the original complemented strain. The lgtB in-frame non polar mutant was constructed by replacing lgtB with GmR gene from ATG to TAA codon. The original complemented strain was constructed by inserting the intact lgtB gene follow by GmR gene into previous constructed ΔlgtB::KanR strain in order to confirm the phenotype of the previous lgtB::KanR mutant. (B) PCR analysis verifying the lgtB in-frame non polar mutant and the original complemented strain. Primers P22 and P23 were used to amplify the locus region of lgtB from the wild type SC096 (lane 1), the lgtB in-frame non polar strain (lane 2), and the original complemented strain (lane 3); lane M shows a 5Kb DNA molecular marker. (C) Survival of lgtB in-frame non polar mutant and the original complemented strains treated with 50% porcine serum. The lgtB in-frame non polar mutant showed significantly increased susceptibility to serum compared with the wild type strain SC096 (p < 0.01) with 50% porcine serum, while the original complemented strain restored the serum resistant phenotype. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. The asterisks indicate that the survival of bacteria in serum was statistically different (p < 0.01) from that of the wild-type SC096 strain as judged by the Student t-test.