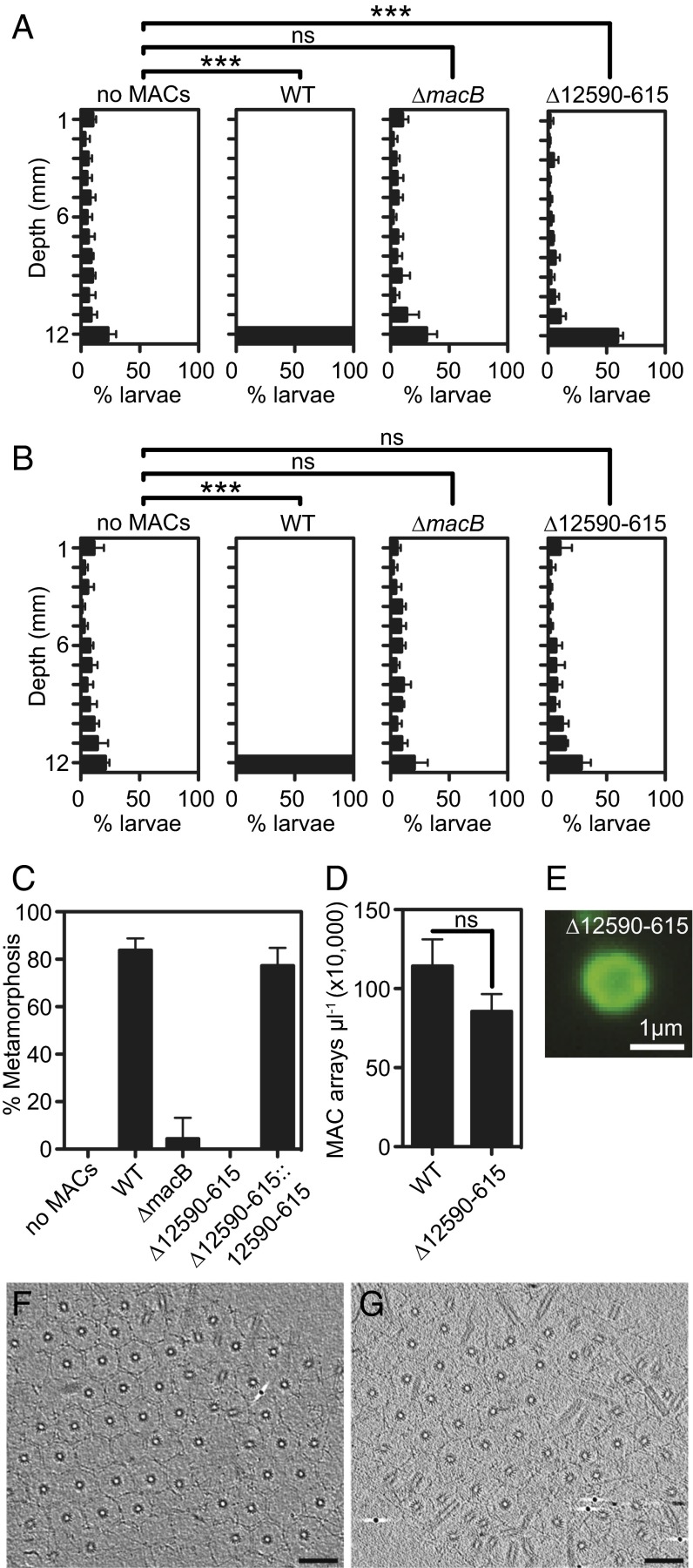
Fig. 2.
Two bacterial loci are required for different stages of metamorphosis. (A and B) MAC extract from wild-type, ∆macB, or ∆12590–615 strains was added to competent larvae in polystyrene cuvettes in a total of 0.5 mL. The vertical distribution of larvae within the cuvette was quantified at 5 min (A) or 30 min (B) after addition of MACs. Artificial seawater without MACs served as a negative control. Error bars indicate SDs of six biological replicates. Twelve to 55 larvae were quantified per replicate. Student’s t test of mean depth: ns, not significant; ***P < 0.00001. (C) Metamorphosis of Hydroides exposed to MAC extract from wild-type, ∆12590–615, ∆macB, or ∆12590–615::12590–615. Error bars are SDs of four biological replicates. (D) Quantification of MAC arrays from extract of wild type or ∆12590–615. Error bars are SDs of three biological replicates. Student’s t test. (E) Image of a fluorescently tagged MAC from ∆12590–615 macB-sfgfp. (F and G) The wild type (F) and ∆12590–615 mutant (G) produce ordered arrays having comparable size and number of MACs. Shown are 9-nm slices through electron cryotomograms (Scale bars, 100 nm).