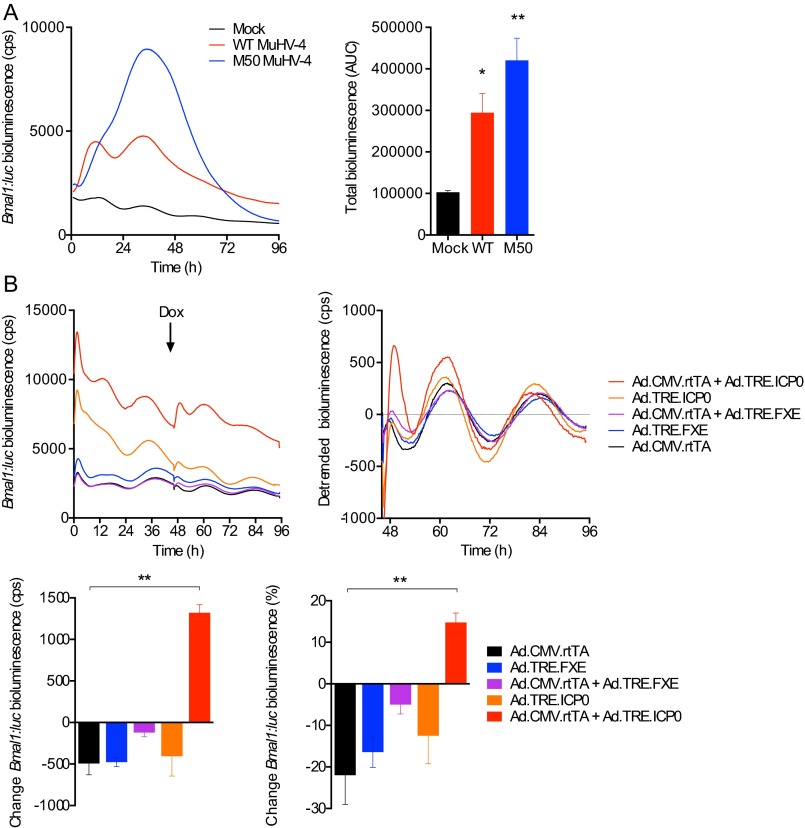
Fig. S7.
Bmal1 expression is induced in cells overexpressing herpesvirus transcriptional activators. (A) Synchronized NIH 3T3 cells expressing Bmal1:luc transcriptional reporter were either mock-infected or infected with WT MuHV-4 or M50 MHV-68, a recombinant virus that overexpresses ORF50, which encodes the main viral transcriptional transactivator. Bmal1:luc bioluminescence is significantly increased during M50 MuHV-4 infection compared with WT MuHV-4 or mock-infected controls (mean ± SEM; n = 3; one-way ANOVA: P = 0.0049; post hoc multiple comparisons: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (B) An adenoviral Tet-On system was used to investigate whether the HSV-1 viral transactivator ICP0 can initiate Bmal1 transcription. Synchronized NIH 3T3 cells expressing the Bmal1:luc transcriptional reporter were infected with adenoviral constructs expressing rtTA from the HCMV IE promoter (Ad.CMV.rtTA), ICP0 under the control of a TRE promoter (Ad.TRE.ICP0), a nonfunctional RING-finger deletion mutant (FXE) of ICP0 under the control of a TRE promoter (Ad.TRE.FXE), or a combination thereof. Doxycycline (Dox) was added 46 h after infection to enable transcription from the TRE promoter if rtTA is present. ICP0 significantly increases Bmal1:luc (% change 3 h pre-Dox vs. 3 h post-Dox addition) compared with controls (mean ± SEM; n = 3; one-way ANOVA: P = 0.0038; post hoc multiple comparisons: **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).