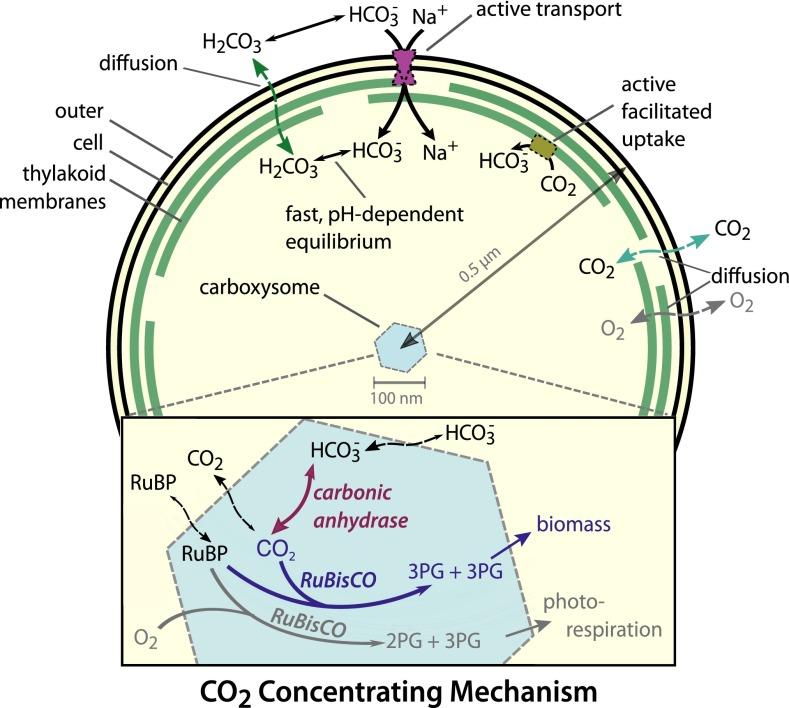
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the generally accepted model of the cyanobacterial CCM. The cyanobacterial CCM concentrates HCO3− in the cytosol via two classes of uptake systems: transporters and facilitated uptake systems. We focus on Na+-activated transporters, which transport one Na+ with each HCO3−. Facilitated uptake of CO2 is catalyzed by proteins on the thylakoid membrane and is thought to couple NAD(P)H oxidation to the vectorial conversion of CO2 into HCO3−. Roughly 250 RuBisCOs (2,000 active sites) and 100 CAs are localized to the carboxysome. HCO3− concentrated in the cytosol enters the carboxysome, where it is converted to a high CO2 concentration by CA activity. This elevated CO2 concentration increases the rate of RuBisCO carboxylation and competitively inhibits oxygenation, increasing the overall efficiency of carbon fixation. For parameter values and model details see SI Appendix. References for each model component are given in the main text. 3PG, 3-phosphoglycerate.