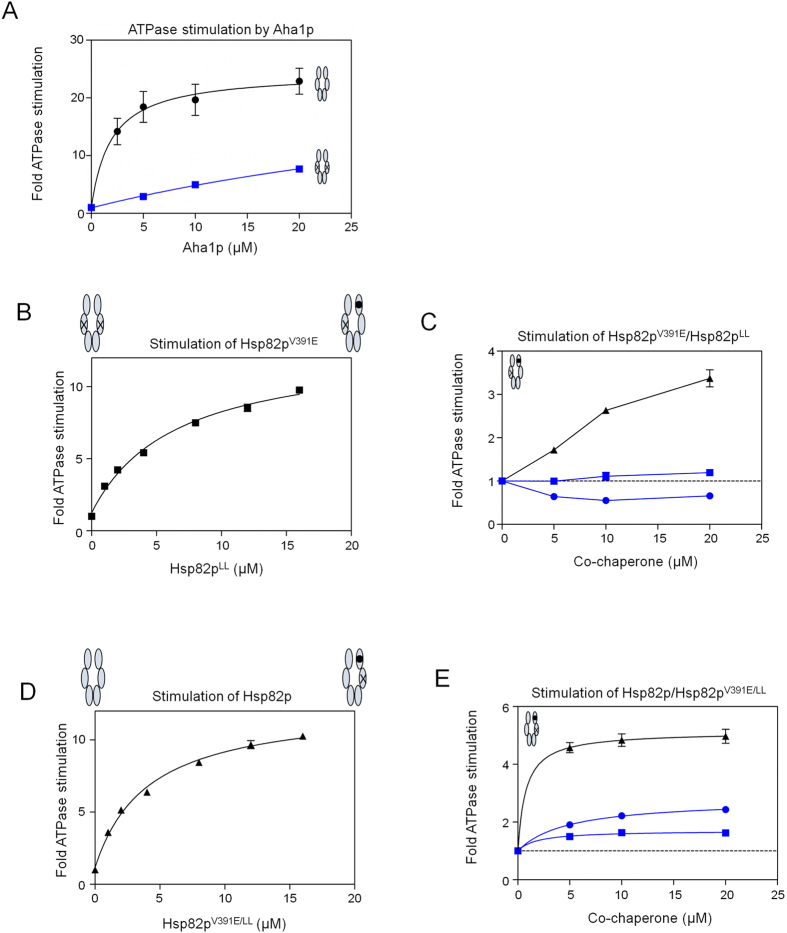
Figure 3. Co-chaperone action is protomer specific; Co-chaperones stimulate the ATPase activity of Hsp82p when co-chaperone binding is restricted to the catalytic protomer, but not the non-catalytic protomer.
(A) Aha1p stimulates wildtype Hsp82p (black) robustly but does not readily stimulate Hsp82pV391E (blue). Reactions contained 2 μM Hsp82p or Hsp82pV391E with indicated Aha1p concentrations. ATPase rate shown as a fold stimulation of Hsp82p or Hsp82pV391E intrinsic rate. (B) The addition of Hsp82pLL potently stimulates the ATPase activity of Hsp82pV391E. Hsp82pLL was titrated into reactions containing 2 μM of Hsp82pV391E. The resulting stimulated ATPase rate is shown as a fold stimulation of the intrinsic Hsp82pV391E rate. (C) Aha1p (black triangles) and Aha1pN (blue squares) do not robustly stimulate the ATPase activity of Hsp82pV391E:Hsp82pLL heterodimers, and Hch1p (blue circles) inhibited the ATPase activity of Hsp82pV391E:Hsp82pLL heterodimers. Heterodimers are formed by mixing 1 μM Hsp82pV391E and 5 μM Hsp82pLL. ATPase rates are shown as a fold stimulation of the intrinsic rate of Hsp82pV391E:Hsp82pLL heterodimers (stippled line). (D) The addition of Hsp82pV391E/LL potently stimulates the ATPase activity of wildtype Hsp82p. Hsp82pV391E/LL was titrated into reactions containing 2 μM of Hsp82p. The resulting stimulated ATPase rate is shown as a fold stimulation of the intrinsic Hsp82p rate. (E) Aha1p (black triangles), Hch1p (blue circles), and Aha1pN (blue squares) stimulates the ATPase activity of Hsp82p:Hsp82pV391E/LL heterodimers. Heterodimers are formed by mixing 1 μM Hsp82p and 5 μM of Hsp82V391E/LL. ATPase rates are shown as a fold stimulation the intrinsic rate of Hsp82p:Hsp82pV391E/LL heterodimers (stippled line).