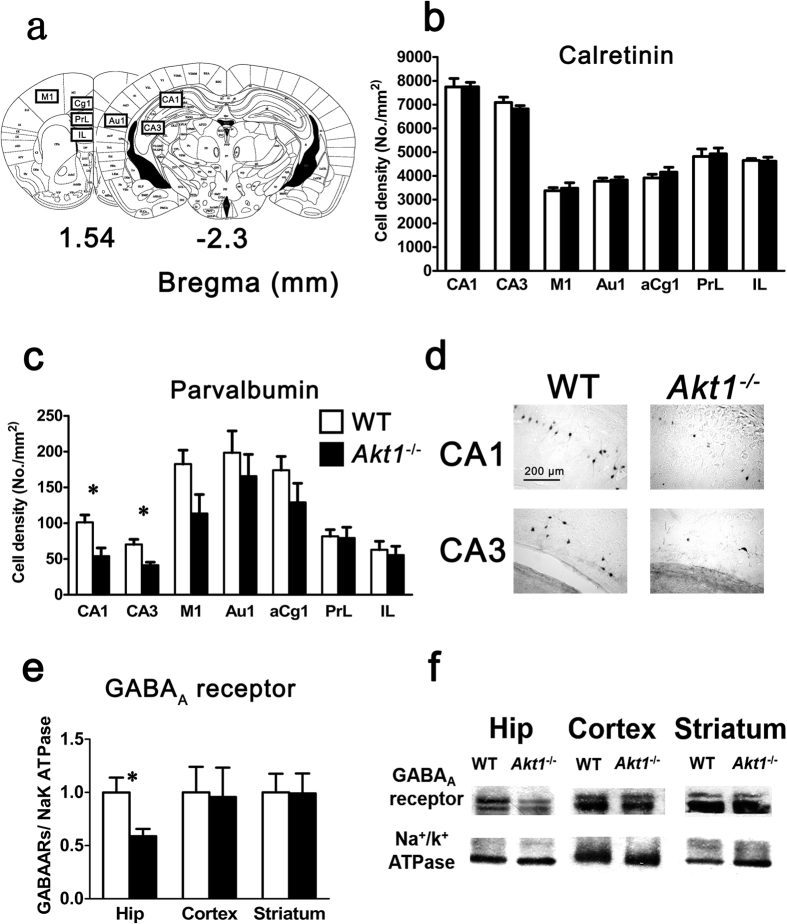
Figure 3. Experiment 3: Reduced numbers (cell density; cells/mm2; mean ± SEM) of parvalbumin-positive interneurons and reduced expression of GABAA receptors were observed in the hippocampus of female Akt1−/− mice (black bar; n = 6) compared to female WT littermate controls (white bar; n = 8).
(a) Mouse brain atlases highlighting the regions of interest: hippocampal CA1 region (CA1), hippocampal CA3 region (CA3), primary motor cortex (M1), primary auditory cortex (Au1), anterior cingulate cortex, area 1 (aCg1), prelimbic cortex (PrL), and infralimbic cortex (IL). (b) Calretinin-positive interneurons in the different brain regions of female mice. (c) Parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the different brain regions of female mice. The cell density in the CA1 and CA3 areas was lower in female Akt1−/− mice than in female WT mice. (d) Representative immunohistochemical images of parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the dorsal hippocampus (CA1 and CA3 areas; scale bar: 200 μm). (e) The expression of functional GABAARs in the hippocampus, cortex, and striatum of female mice. A significant difference in functional GABAAR expression in the hippocampus was found between Akt1−/− and WT females. (f) Representative Western blot images of functional GABAAR expression (GABAAR: GABAAR β2 subunit; Na+/K+ ATPase: loading control for membrane proteins). *p < 0.05.