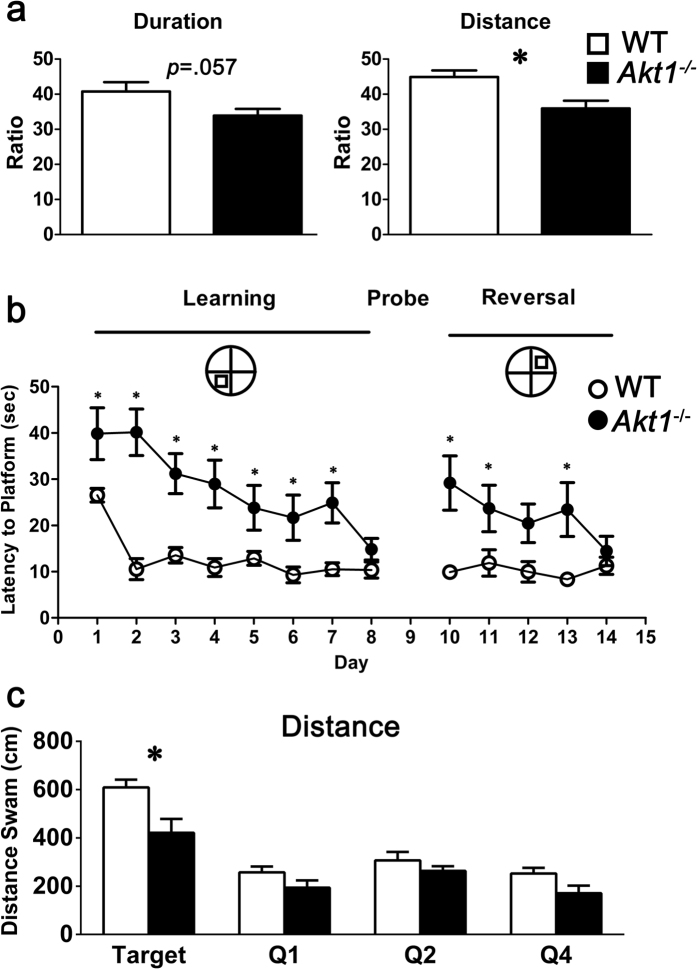
Figure 6. Female Akt1−/− mice exhibited impaired hippocampus-related cognitive performance on the Y-maze (Experiment 6a) and Morris water maze tasks (Experiment 6b).
(a) The percentages (%, mean ± SEM) of time spent and distance travelled in the novel arm of the Y-maze. Female Akt1−/− mice (black bars; n = 8) exhibited reduced relative duration and distance in the novel arm of the Y-maze compared to female WT littermate controls (white bars; n = 8). (b) The escape latency (mean ± SEM sec) to reach the hidden platform in the Morris water maze task. Female Akt1−/− mice (black circles; n = 8) showed impairments in acquisition and reversal learning in the Morris water maze test. (c) Female Akt1−/− mice swam a shorter distance in the target quadrant than female WT controls on the probe test (Day 9). *p < 0.05.