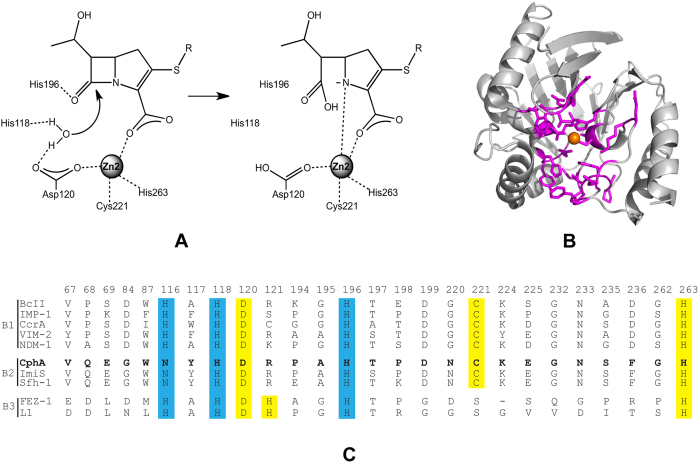
Figure 1. Active site residues of metallo-β-lactamases.
(A) Schematic representation of carbapenem substrate binding and anionic intermediate stabilization in the active site of mono-zinc metallo-β-lactamase CphA. An active site water interacts with Asp120 and His118 and is activated for attack on the carbonyl carbon of the carbapenem, whose carbonyl group is polarized by interaction of the carbonyl oxygen with His196. After C-N bond cleavage, anionic nitrogen is stabilized by interactions with the zinc ion. (B) Diagram of the CphA β-lactamase structure highlighting active site residues for which random mutant libraries were created. The zinc atom is represented as an orange sphere. The figure was rendered with the Pymol program using coordinates from the Protein Data Bank accession code 1X8G 7. (C) Sequence alignment of representative metallo-β-lactamases from subclasses B1, B2, and B3. The residues in blue boxes and yellow boxes indicate the histidine and cysteine zinc binding site residues, respectively. CphA residues are in bold.