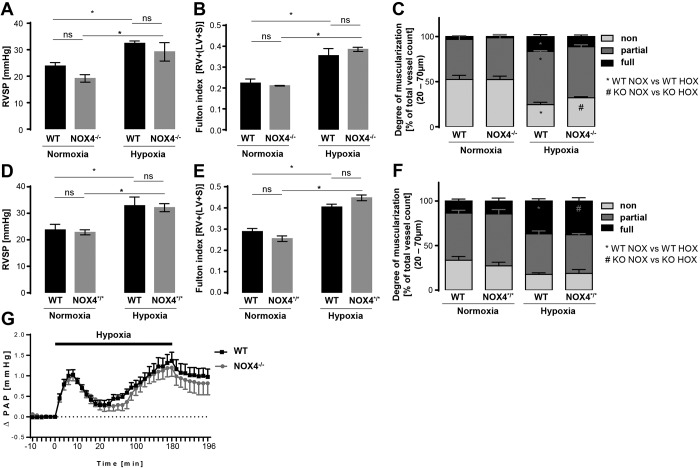
Figure 1.
Chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension and hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in wild-type (WT), NOX4−/− (constitutive Nox4 knockout) and NOX4*/* (global tamoxifen-inducible [Nox4flox/flox-ERT2-CRE/0] Nox4 knockout) mice. A, D, Right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP, mmHg) in normoxic (21 days at 21% O2) and chronic hypoxic (21 days at 10% O2) WT and NOX4−/− (n = 5–6; A) and NOX4*/* (n = 6–8; D) mice. *p < 0.05 (significantly different); ns: not significantly different. B, E, Fulton index, depicted by the ratio of right ventricle mass to (left ventricle + septum) mass (RV/(LV + S)), in normoxic and chronic hypoxic WT and NOX4−/− (n = 2–6; B) and NOX4*/* (n = 6–9; E) mice. *p < 0.05 (significantly different); ns: not significantly different. C, F, Vascular remodeling of normoxic and chronic hypoxic WT and NOX4−/− (n = 5–6; C) and NOX4*/* (n = 5–6; F) mice quantified by the degree of muscularization of small (outer diameter of 20–70 μm) pulmonary arterial vessels. Vessels were categorized as fully muscularized (>70% vessel media α-SMA positive), partially muscularized (>5% but ≤70% vessel media α-SMA positive), or nonmuscularized (≤5% vessel media α-SMA positive) after immunostaining against α-SMA and von Willebrand factor. One hundred vessels from each lung were analyzed. An asterisk indicates significant difference between normoxic (NOX) and hypoxic (HOX) WT mice; a pound sign indicates significant difference between NOX and HOX NOX4−/− (KO) mice (p < 0.05). G, Time course of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in isolated, buffer-perfused, and ventilated mouse lungs during 180 minutes of hypoxic (1% O2) ventilation. Changes in pulmonary arterial pressure (ΔPAP, mmHg) are depicted for WT and NOX4−/− mouse lungs (n = 8). α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin.