Figure 3.
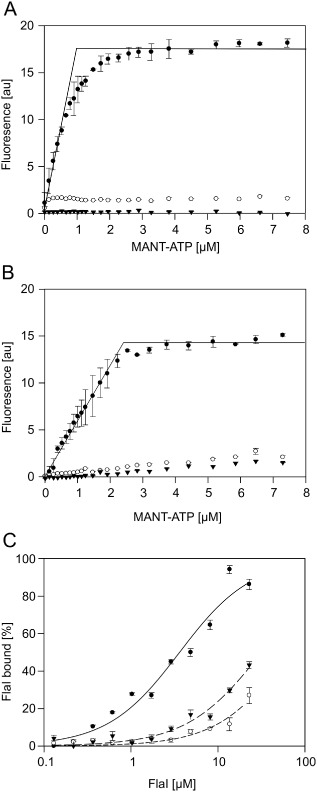
Mutations in the FlaH Walker A and B Motifs strongly reduce nucleotide binding and interaction with FlaI. The increase in fluorescence upon MANT‐ATP binding to 1 μM FlaH was determined for increasing MANT‐ATP concentrations for (A) WT SaFlaI (closed circles), SaFlaH K33A (open circles) and SaFlaH D122N (triangles) and (B) WT PfFlaH (closed circles) PfFlaH K53A (open circles) and PfFlaH D140N (triangles). (C) The binding of PfFlaH to PfFlaI was studied by microscale thermophoresis. The 34 nM labeled WT PfFlaH, PfFlaH K53A or PfFlaH D140N were mixed with increasing concentrations (14 nM–29 μM) of unlabeled PfFlaI, and thermophoresis was performed. Curves were obtained from at least two independent experiments. Binding curves were fitted to the Hill equation, and binding is depicted as the fraction bound.
