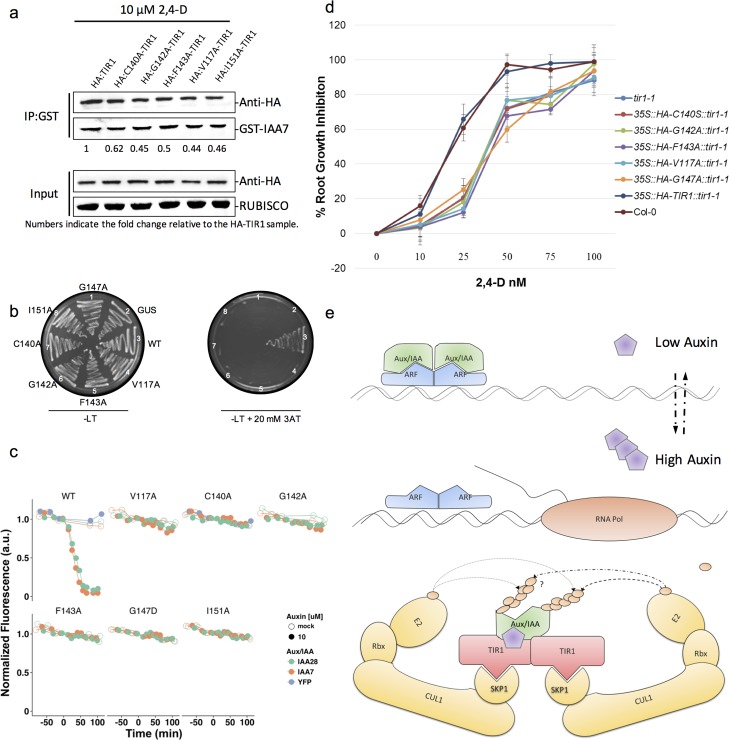
Fig 4. TIR1 oligomerization is essential for auxin signaling.
(a) Semi in vitro pull-down assays using GST-IAA3 and Nicotiana cell extracts expressing wild-type and mutant HA:TIR1 proteins. Values represent fold-change compared to TIR1:HA samples (all values were corrected for equal loading among samples). (b) Assessment of TIR1-IAA7 protein interaction in Y2H assay in the presence of auxin (25 μM). Images of yeast cells expressing the designated constructs and grown on histidine plates and test plates containing 10 mM of 3-AT. (c) Degradation of YFP-IAA fusion proteins in yeast in the presence of wild-type and mutant TIR1 proteins after the addition of auxin. Yeast cells were imaged using time-lapse flow cytometry. Degradation curves were normalized to the starting fluorescence absorbance unit (a.u.). (d) Five day old seedlings were transferred to 0.5x MS mediums containing the indicated concentrations of 2,4-D. After 5 days of growth, the length of primary root was measured, and expressed relative to growth on control plates. (e) Schematic model of SCFTIR1 dimerization.