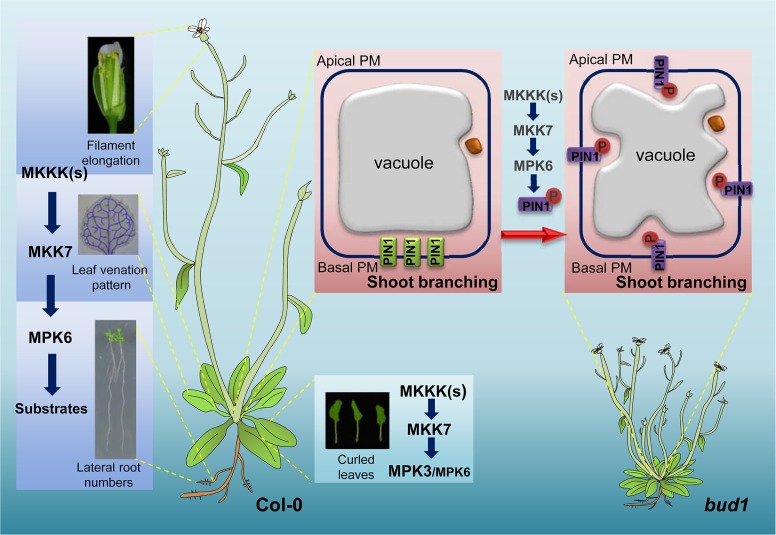
Fig 8. A proposed working model of the MKK7-MPK6/3 cascade involved in plant development in Arabidopsis.
The MKK7-MPK6 cascade plays predominant roles in diverse developmental processes including leaf venation architecture, filament elongation, lateral root formation, and shoot branching. MKK7-MPK3 and MKK7-MPK6 cascades function redundantly in leaf morphology; the MKK7-MPK6 signaling pathway regulates PAT through phosphorylating PIN1. In the wild type, PIN1 basal localization is controlled by reversible phosphorylation of S337 site by the MKK7-MPK6 cascade. In the bud1 plants, constitutively activated MKK7-MPK6 signaling leads to sustained phosphorylation of the PIN1 S337 site, which leads to PIN1 apolar localization and results in branching phenotype.