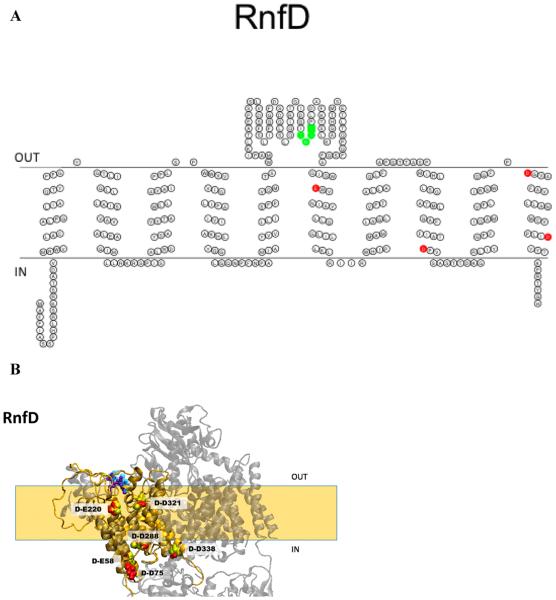
Figure 7.
(A) Membrane topology model of RnfD. Acidic residues implicated in sodium binding and release are colored red (E220, D288, D321, and D338). The FMN binding site is colored green (T184, M185, A186, and T187). (B) Homology model of RnfD superimposed on the NqrB structure. The acidic residues implicated in sodium transport in Na+-NQR are labeled in RNF (red) and Na+-NQR (yellow) structures [RnfD-E220 (NqrB-E274), RnfD-D288 (NqrB-D346), RnfD-D321 (NqrB-D380), and RnfD-D388 (NqrB-D397)]. The FMN binding site is also shown [RnfD-T184 (NqrB-S233), RnfD-M185 (NqrB-G234), RnfD-A186 (NqrB-A235), and RnfD-T187 (NqrB-T236)]. The model created using RaptorX was selected as the best model; this selection was made on the basis of comparison to our RnfD topology data and the crystallographic structure of Na+-NQR.