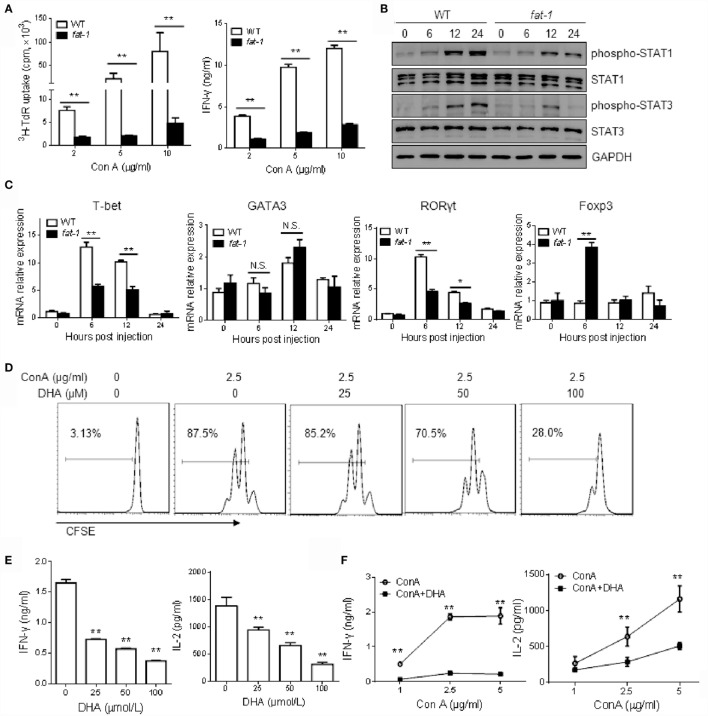
Figure 4.
n-3 PUFAs inhibit Con A-stimulated T cell activation in vitro. (A) Hepatic MNCs from WT and fat-1 transgenic mice were stimulated with different concentration of Con A in vitro. The proliferation response and cytokine production of T cells were determined by [3H] thymidine uptake and ELISA assay, respectively. **p < 0.01. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (B,C) Hepatic MNCs were treated with Con A (5 μg/ml) for various time. Cell extracts were then subjected to western blotting analysis with the antibodies against phospho-STAT1, phospho-STAT3, STAT1, and STAT3. One of the three independent experiments is shown (B). Relative mRNA expression of T cell transcript factors, including T-bet, GATA3, RORγt, and Foxp3, was measured by quantitative RT-PCR analysis and expressed as a ratio to GAPDH. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, N.S., not significant. One of the three independent experiments is shown (C). (D,E) Liver MNCs isolated from WT mice were cultured with Con A (2.5 μg/ml) in the presence of indicated doses of DHA. T cell proliferation was measured by CFSE dilution (D), and cytokine levels were determined by ELISA assays (E). **p < 0.01, compared to the group without DHA. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (F) Liver MNCs isolated from WT mice were stimulated with Con A at different concentrations with or without DHA (50 μmol/L) incubation, and the cytokine production was evaluated by ELISA. **p < 0.01, compared to the group without DHA. Data shown represent three independent experiments with similar results.