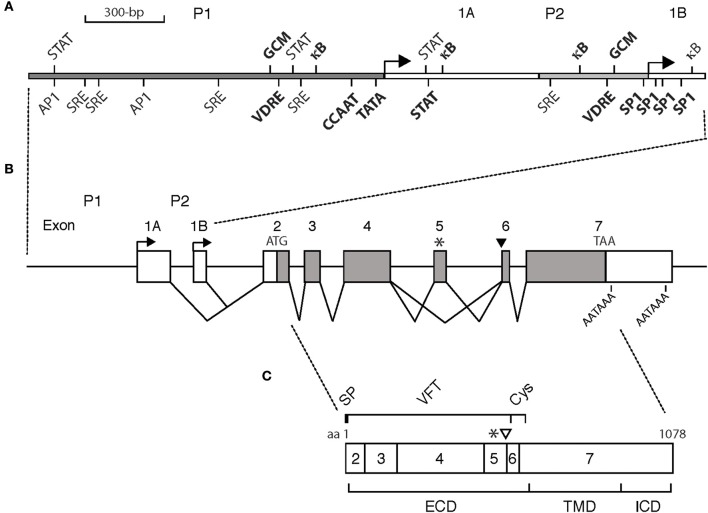
Figure 1.
Schematic of (A) the CASR gene promoters, (B) the CASR gene exon/intron organization, and (C) CaSR protein. (A) Promoter P1 and P2, gray bars. Exons 1A and 1B, white bars. Transcription start sites, arrows. CCAAT and TATA boxes, and SP-1 sites driving transcription of exon 1A and 1B, respectively, are bolded. Cis-acting elements are shown. VDRE, vitamin D response element; κB, kappa-B element responsive to nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; GCM, glial cells missing; AP1, activator protein 1; SRE, serum response element. Bolded: those shown to be functionally active. Not bolded: those predicted but either not functionally active or not yet evaluated. Not all predicted cis-acting elements are shown. (B) Exon/intron organization of the CASR gene. Exons are drawn to scale introns are not. White bars: mRNA untranslated (exons; 1A, 1B, part of 2, part of 7). Gray bars: mRNA protein coding (exons; part of 2, 3-6, part of exon 7). ATG: initiation codon. TAA: stop codon. AATAAA: polyadenylation signals. Alternative splicing of exons 1A and 1B to exon 2 is shown. Asterisk, *: alternative transcript lacking exon 5. Black arrowhead: alternative transcript having additional 30 bases at the beginning of exon 6. (C) CaSR protein: 1078 amino acid (aa) protein encoded by exons 2-7. Asterisk, *: minus 77 aa encoded by exon 5. Open arrowhead: additional 10 aa encoded by extra 30 bases of alternative RNA transcript. SP, signal peptide; VFT, venus flytrap domain; Cys, cysteine rich domain; ECD, extracellular domain; TMD, transmembrane domain; ICD, intracellular domain.