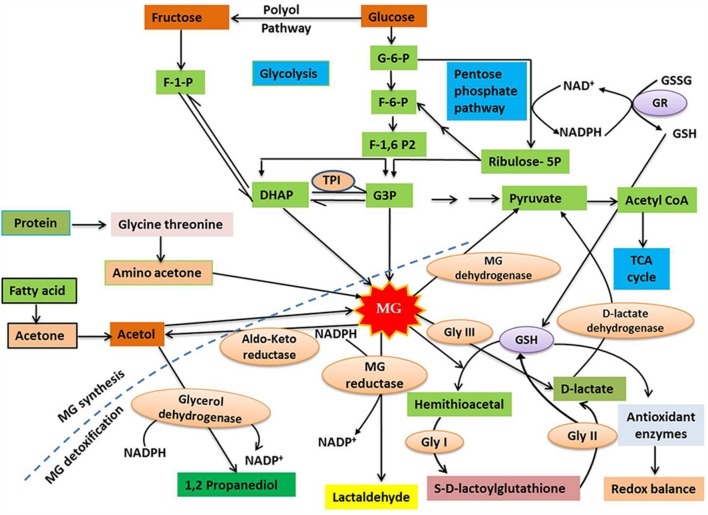
FIGURE 1.
A diagrammatic representation of methylglyoxal (MG) synthesis and detoxification in plants (modified from Ko et al., 2005; Hossain et al., 2011). MG is primarily produced as a by-product of carbohydrate metabolism, with small amount produced during protein and lipid metabolism. Cytotoxic MG is efficiently degraded to form D-lactate by the action of the enzymes Gly I and Gly II, with the help of GSH. In addition, GSH-independent Gly III is able to convert MG to D-lactate. D-lactate dehydrogenase finally converts D-lactate into pyruvate, which enters TCA cycle via acetyl CoA. The broken line separates the synthesis and detoxification pathways of MG. For further discussion, see the text. Abbreviations are defined in the text.