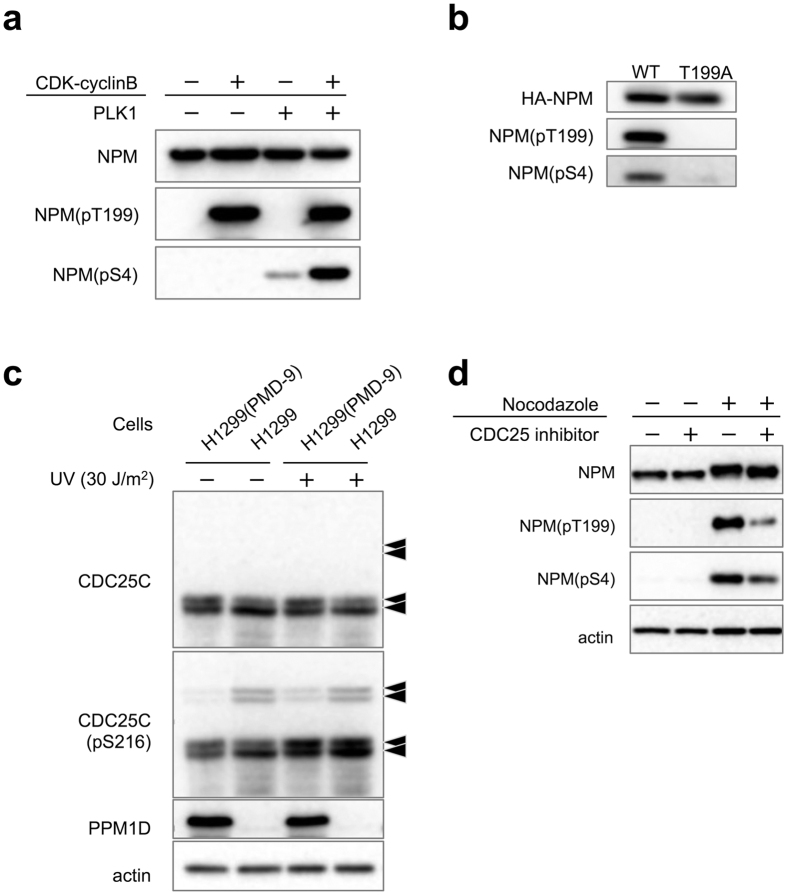
Figure 5. Signalling cascade in PPM1D-overexpressing cells.
(a) In vitro sequential phosphorylation of NPM by CDK1-PLK1. His-NPM were expressed in E. coli and purified. 2 μg of His-NPM were incubated with 10 units of CDK1-cyclinB for 60 min at 30 °C, prior to incubation with 100 ng of PLK1 for 60 min at 30 °C. 2x sample buffer was added to stop the reaction. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and were subjected to Western blotting with same antibodies as in Fig. 3. (b) In vivo sequential phosphorylation of NPM. MCF-7 cells were transfected with either HA-NPM(WT) or HA-NPM(T199A) for 40 h then treated with 4 μg/ml nocodazole for 16 h. Lysates were then purified with mouse monoclonal anti-HA and analysed by Western blotting with polyclonal anti-HA and the same antibodies as Fig. 3. (c) Decrease of phosphorylated-CDC25C at Ser216 by PPM1D overexpression in H1299 clones. All arrows indicate CDC25C with different modification states. Cells were lysed 2 h after exposure to 30 J/m2 of UV radiation and analysed by Western blotting with rabbit monoclonal anti-CDC25C(pS216) and the same antibodies as Fig. 3. (d) Decrease of phosphorylated-NPM at Thr199 and Ser4 by CDC25 inhibitor in MCF-7. Cells were treated with 3 μM CDC25 inhibitor for 6 h and subsequently treated with 4 μg/ml nocodazole for 16 h. Cells were then harvested by mitotic shake off and analysed by Western blotting with mouse monoclonal anti-NPM, rabbit polyclonal anti NPM(pT199), rabbit monoclonal anti-NPM(pS4), and mouse monoclonal anti-actin.