Fig. 3.
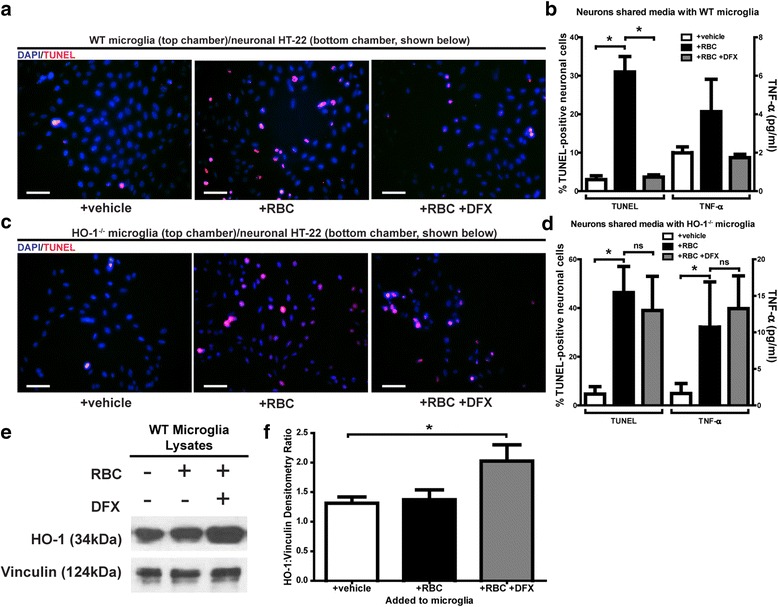
Microglial HO-1 has a role in deferoxamine protection from red blood cell (RBC)-induced neuronal damage—Trans-wells with WT or HO-1−/− primary microglia were plated with hippocampal neurons (HT-22) and treated with vehicle, red blood cells (RBCs), or RBCs with DFX. a Representative TUNEL (red) stained images of neurons from each WT primary microglia trans-well with DAPI (blue) nuclei counterstain (all scale bars = 20 μm). b Quantification of TUNEL-positive neurons and TNF-α concentration from each WT primary microglia trans-well; RBC exposure significantly increased neuronal damage while DFX significantly reduced this RBC-induced damage (one-way ANOVA P < 0.05; *P < 0.05; n = 3 per group). Trend towards increased TNF-α production in the trans-well assays incubated with RBCs (one-way ANOVA P < 0.05; n = 3; b); trend towards decreased TNF-α production in the trans-well assays treated with DFX after RBC exposure (n = 3; b). c TUNEL stained images of neurons from each HO-1−/− primary microglia trans-well with DAPI nuclei counterstain. d Quantification of TUNEL-positive neurons and TNF-α concentration from each HO-1−/− primary microglia trans-well; RBC exposure significantly increased neuronal damage as well as TNF-α production, and DFX did not reduce this RBC-induced damage or TNF-α concentration (one-way ANOVA P < 0.05; *P < 0.05; n = 3 per group). e Western blot of primary microglial lysates from each group. f Quantification of bands from Western blot of primary microglial lysate; showed that HO-1 protein expression significantly increased in WT primary microglia culture exposed to RBCs with DFX (one-way ANOVA P < 0.05; *P < 0.05; n = 3 per group)
