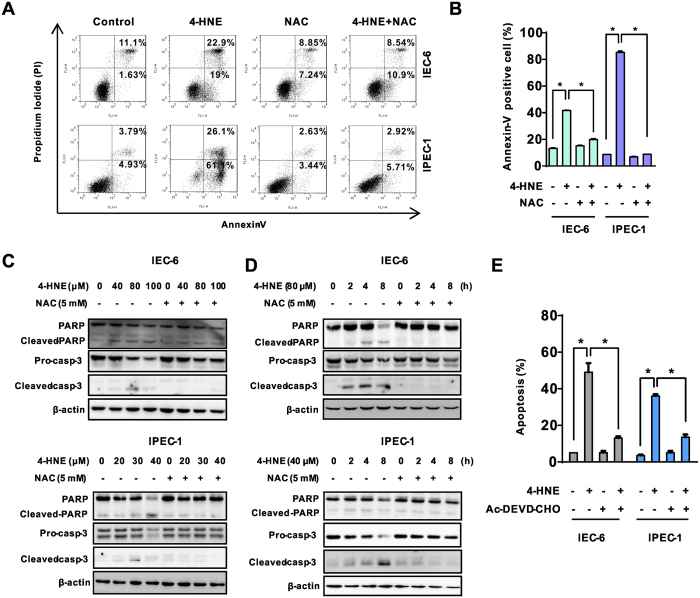
Figure 2. The protective effect of NAC on 4-HNE-induced cell death was associated with inactivation of caspase-3-dependent apoptosis.
(A) Cells pretreated with or without NAC (5 mM) in serum-free medium for 2 h and then were exposed to 4-HNE (80 μM for IEC-6 and 40 μM for IPEC-1, respectively) for an additional 8 h. Cell apoptosis was evaluated using the Annexin-V/PI double staining kit by flow cytometry. (B) Statistical analysis for Annexin-V positive cells treated as in Fig. 2A. Values are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3), *p < 0.01. (C) Immunoblotting analysis of pro-caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3 and PARP in cells treated with indicated concentrations of 4-HNE for 8 h in the presence or absence of NAC pretreatment (5 mM). (D) Immunoblotting analysis for pro-caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3 and PARP in cells treated with 4-HNE (80 μM for IEC-6 and 40 μM for IPEC-1, respectively) with or without NAC pretreatment for indicated time periods; β-actin was used as a loading control. (E) Caspase-3 inhibitor Ac-DEVD-CHO protected cells from 4-HNE-induced apoptosis. Cells pretreated with Ac-DEVD-CHO (50 μM) for 1 h were treated with 4-HNE (80 μM for IEC-6 and 40 μM for IPEC-1, respectively) for 8 h and and cell apoptosis was determined by Hoechst 33342/PI double staining. Values are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3), *p < 0.01.