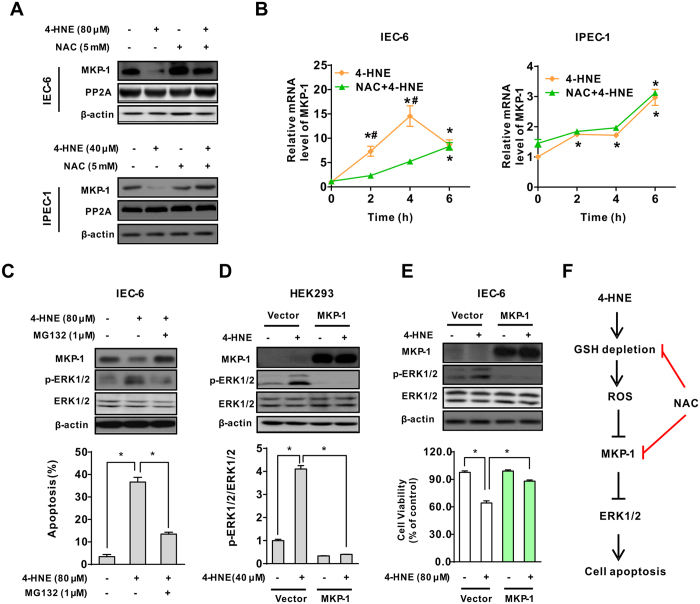
Figure 7. MKP-1 was a critical regulator modulating ERK1/2 activation following exposure to oxidant.
(A) NAC prevented 4-HNE-induced MKP-1 down-regulation. Cells pretreated with NAC (5 mM, 2 h) were exposed to 4-HNE, the protein levels of MKP-1 and PP2A were determined using indicated anti-bodies. β-actin was used as the loading control. (B) Relative mRNA levels of MKP-1 in intestinal epithelial cells. IEC-6 (left panel) or IPEC-1 (right panel) cells pretreated with or without NAC were treated with 4-HNE, qRT-PCR was performed to determine the mRNA levels of MKP-1. β-actin was used as the reference control. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 3), *p < 0.01 compare with that of 0 h control of the same treatment. 4-HNE treatment control, #p < 0.01 compared with that of 4-HNE alone at the same time point. (C) Protein degradation inhibitor blocked 4-HNE-induced MKP-1 down-regulation, ERK1/2 phosphorylation and apoptosis. IEC-6 cells were left untreated or treated with 4-HNE in the presence or absence of a proteolysis inhibitor MG132 (1 μM). The protein levels of MKP-1, ERK1/2, and p-ERK1/2 were determined. β-actin was used as the loading control. Cell apoptosis was evaluated by Hoechst 33342/PI staining. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3), *p < 0.01. (D) MKP-1 repressed 4-HNE-induced ERK1/2 activation. HEK293 cells transfected with empty vector or MKP-1 vector were treated with 4-HNE for 2 h. The protein levels of MKP-1, ERK1/2, and p-ERK1/2 were determined. β-actin was used as the loading control. (E) Overexpression of MKP-1 abolished 4-HNE-induced ERK1/2 activation and cell death. IEC-6 cells transfected with empty vector or MKP-1 vector were treated with 4-HNE. The protein level of MKP-1, ERK1/2, and p-ERK1/2 (upper panel) and cell viability (lower panel) were determined. Values are mean ± SEM, *p < 0.01. (E) Proposed mechanism responsible for 4-HNE-induced apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells.