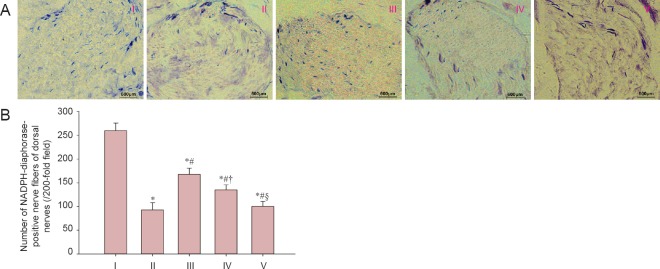
Figure 4.
LBP effect on NOS-containing nerve fibers in rats after cavernous nerve crush injury.
(A) Images of NADPH-diaphorase staining of dorsal nerves for each group. (B) NADPH-diaphorase-positive nerve fibers. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey post-hoc tests were used to assess differences between groups. *P < 0.05, vs. sham group; #P < 0.05, vs. injured group; †P < 0.05, vs. experimental A group; §P < 0.05, vs. experimental B group. In experimental A, B, and C groups, the rats were intragastrically administered LBP (10 mg/kg/d) for 2 consecutive weeks at 1, 7, and 14 days post-injury. NOS: Nitric oxide synthase; NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. I: Sham; II: injured; III: experimental A; IV: experimental B; V: experimental C.