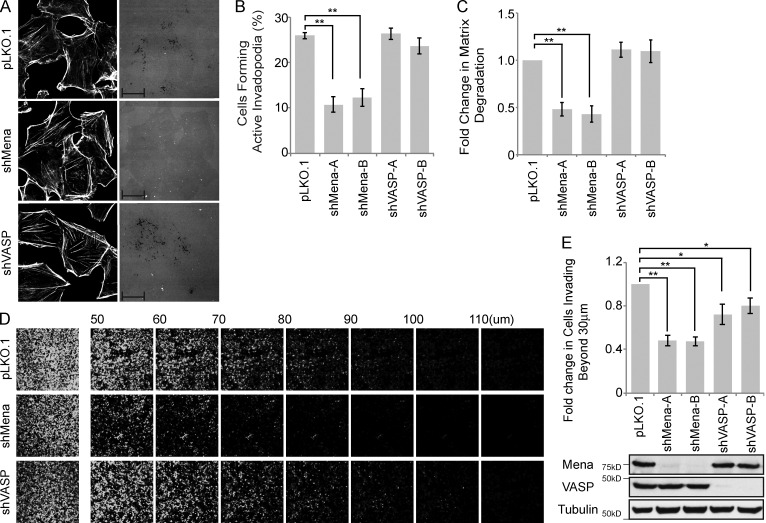
Figure 6.
Mena, but not VASP, promotes proteolytically active invadopodia formation and cell invasion. (A–C) MDA-MB-231 cells were stably transduced with pLKO.1 or two individual shRNA duplexes targeting Mena or VASP. (A) Cells were seeded on fluorescently labeled gelatin and stained with phalloidin (F-actin), and confocal images were acquired. (B) The percentage of VASP- or Mena-knockdown cells that formed proteolytically active invadopodia was quantified in comparison to control cells. (C) Amounts of ECM degradation by VASP- or Mena-knockdown cells were quantified as fold change compared with control cells. (D) MDA-MB-231 cells stably transduced with pLKO.1 or individual shRNA duplexes targeting VASP or Mena were subjected to an inverted invasion assay. Representative confocal z-stacks depict relative cell invasion. (E) For quantification of cell invasion, five confocal z-stacks per condition per experiment were acquired. Fluorescence intensity of the planes within each z-stack was measured using Cell Profiler software. Cells invading to and past 30 µm inside the matrix were quantified as percentage of total cell population. Experiments were repeated four times. Western blot reveals the relative protein levels of VASP and Mena between different MDA-MB-231 cells stably transduced with pLKO.1 and individual shRNA duplexes targeting VASP or Mena. All quantified data indicate the mean values ± SE from at least three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. Bars: 10 µm; (inset) 2 µm.