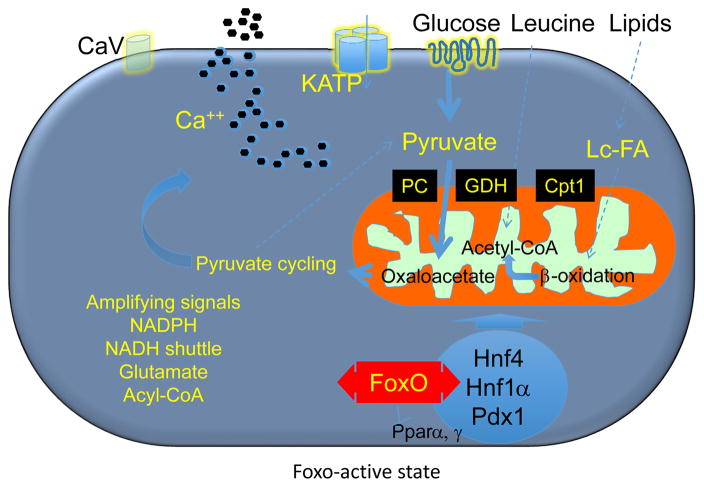
Figure 2. Model of Foxo (1, 3a, 4) role in physiologic β-cell function.
In the early phases of diabetes, Foxo nuclear translocation mediates the effects of glucose on gene expression through MODY gene networks, allowing glucose flux into mitochondria for ATP production (thick arrows), while limiting the contributions by lipids and amino acids (thin dotted arrows). This situation likely prevents the generation of toxic metabolic intermediates that can be detrimental to β-cell health.