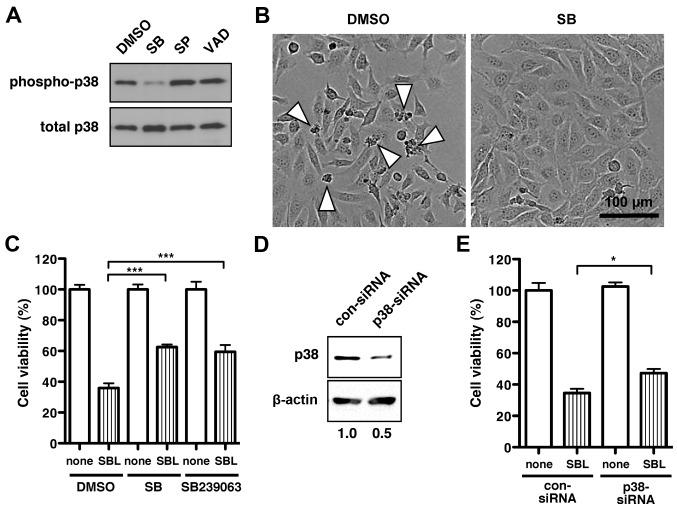
Figure 2.
Inhibition of p38 MAPK activation and expression suppresses SBL-induced cell death in MDA-MB231 cells. (A) Immunoblot analysis of phosphorylated p38 MAPK (upper panel) and total p38 MAPK (lower panel) in MDA-MB231 cells treated with 2 μM SBL in the presence of 1% (v/v) solvent (DMSO), 10 μM SB203580 (SB), 10 μM SP600125 (SP), or 100 μM zVAD-fmk (VAD) for 72 h. (B) Cell morphology of MDA-MB231 cells after treatment with 2 μM SBL for 72 h in the presence of DMSO or 10 μM SB. Arrowheads indicate dying or dead cells. (C) Cell viability after treatment with or without SBL for 72 h in the presence of DMSO, 10 μM SB or 10 μM SB239063. The relative cell viability of cells with no treatment with SBL (none) in each sample, was set at 100%. ***P<0.001. (D) Cell lysates treated with control siRNA (con-siRNA) or p38 MAPK-specific siRNA (p38-siRNA) were subjected to immunoblotting to detect endogenous p38 MAPK and β-actin. The numbers at the bottom indicate the ratio of the intensity of p38 MAPK to the intensity of β-actin in each sample, which was 1.0 for con-siRNA-treated cells. (E) The viability of cells treated with con-siRNA or p38-siRNA. The relative cell viability of cells with no treatment with SBL for 48 h (none) in each sample was set at 100%. Results are the means ± SD for three independent experiments conducted in triplicate. *P<0.05.