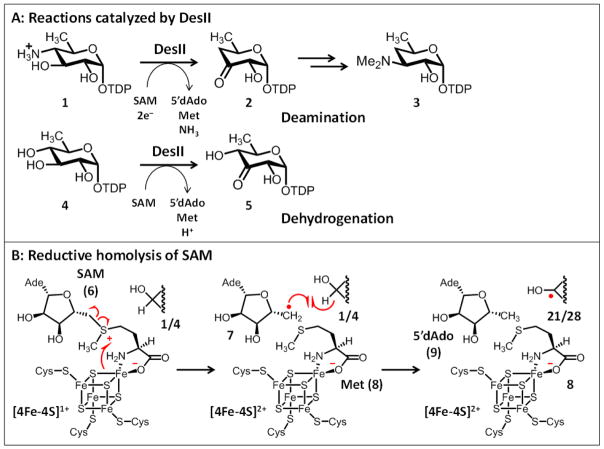
Figure 1.
A, Reactions catalyzed by DesII. B, The reductive homolysis of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (6, Ade: adenine) by an active site [4Fe-4S]1+ cluster is the principle step that characterizes nearly all radical SAM enzymes currently under study including DesII.6,7,12 This results in the formation of L-methionine (Met, 8) and a 5′-deoxyadenosyl radical (7). The latter can then generate additional radical intermediates such as 21/28 in the case of DesII via H-atom abstraction.