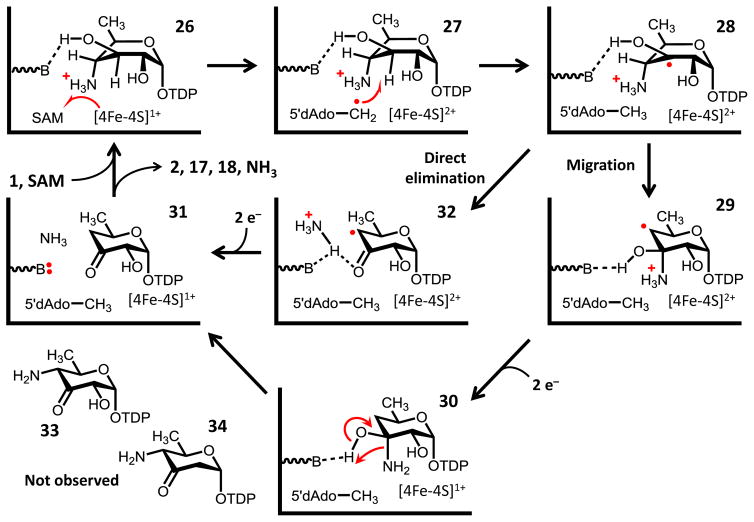
Figure 6.
Working model for the deamination of TDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-D-glucose (1) by DesII. In contrast to TDP-D-quinovose (4, see Fig. 4), 1 is proposed to bind within the DesII active site in a configuration that optimizes the overlap between the partially filled p-orbital at C3 and the C–NH3+ bond at C4, but not the C–OH bond at C2 (see 28). The substrate radical is thus primed for elimination via either direct elimination or migration, and neither dehydrogenation nor dehydration take place to generate ei ther 33 or 34, respectively. Transformations are depicted with only single arrows for simplicity; however, steps may in fact be freely reversible.