FIG 3.
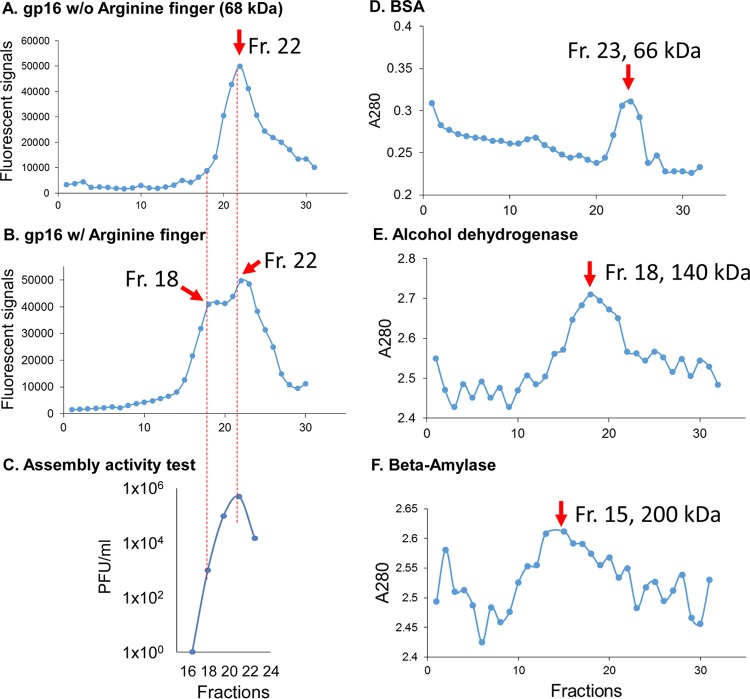
Ultracentrifugation assay showing the presence of both dimers and monomers in gp16 ATPase rings. (A and B) One peak of eGFP-gp16 R146A (A) and two peaks of eGFP-gp16 wild type (B) were shown after parallel ultracentrifugation in a 15% to 35% glycerol gradient, indicating that both monomers and dimers were formed in the gp16 wild type, while dimer formation is interrupted by the mutation of the arginine finger. (C) The isolated gp16 dimers did not show any viral assembly activity, supporting the previous finding that addition of fresh gp16 monomers is required for reinitiating the DNA packaging intermediates. (D to F) Ultracentrifugation fractions (Fr) of protein markers, including BSA (66 kDa), alcohol dehydrogenase (140 kDa), and beta-amylase (200 kDa), are shown, with their peak locations around fractions 23, 18, and 15, respectively, to mark the separation of the monomer and dimer of gp16 ATPase. w/, with; w/o, without.