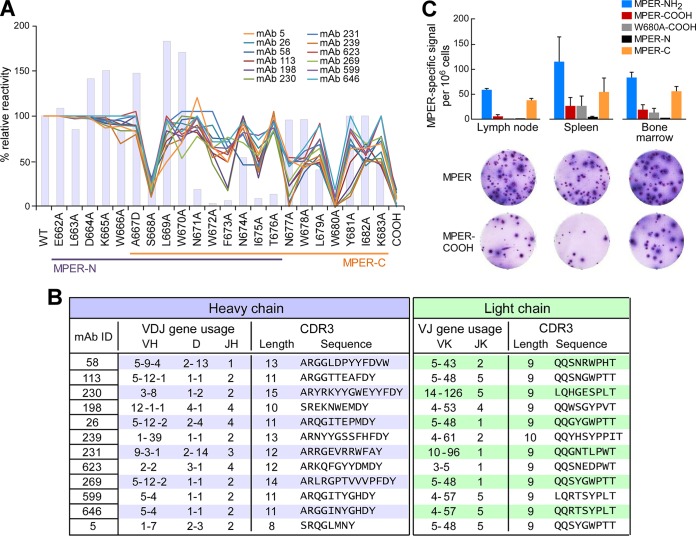
FIG 5.
rMAb epitope mapping analysis reveals convergence to a common epitope at the C-terminal region of the MPER and use of various CDRH3 lengths. (A) Epitope specificity analysis by BIAcore of 12 representative rMAbs by use of liposome-bound serial single alanine MPER mutants. The y axis shows the percent relative binding activities of Abs against each single-residue mutant compared to that of wild-type MPER (WT) (100%). Colored lines represent the epitope specificities of MPER/liposome immunization-derived antibodies, and bars represent the BNAb 10E8. (B) IgH (blue table) and IgLk (green table) V(D)J gene usage and CDR3 analysis of the 12 representative rMAbs from panel A. The germ line gene segment usage, CDR3 lengths, and sequences of the MPER-specific Abs were determined via IMGT/HighV-QUEST analysis. (C) Frequencies of MPER-specific ASCs with different specificities in various organs 5 days after the second immunization with Npalm-MPER/liposomes. Numbers of MPER-binding ASCs were determined by ELISPOT assay, using each of the different epitope-specific MPER/liposomes as the capture antigen. MPER-NH2 and MPER-COOH indicate the HXB2 MPER with C-terminal NH2 and COOH ends, respectively, and W680A-COOH indicates a W680 mutation to A with a C-terminal COOH. The MPER-N (E662 to T676) and MPER-C (A667 to K683) sequences are indicated in panel A.