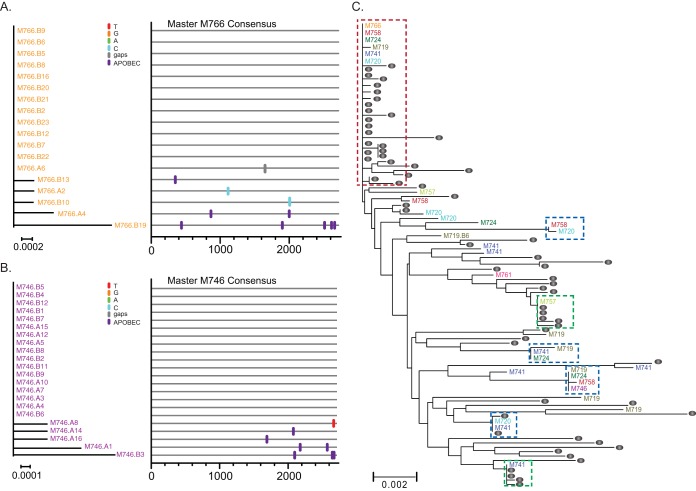
FIG 1.
(A and B) Phylogenetic trees and highlighter alignments of Env sequences from SIvmac251-infected rhesus macaques M766 (A) and M746 (B). Single nucleotide polymorphisms to the consensus sequences are denoted by colored tick marks; gaps are shown in gray and G-to-A mutations in purple. (C) Phylogenetic tree of the 33 T/F env variants (color coded by animal identifier) and sequences from the infection stock used in this study (gray circles). One large cluster (boxed in red) contains 20% of the T/F viruses and 32% of the stock sequences with identical or nearly identical envelopes. The green boxes indicate inoculum-enriched clusters, and the blue boxes indicate transmission-enriched clusters. Nucleotide differences in phylogenetic trees are shown by the scale bar.