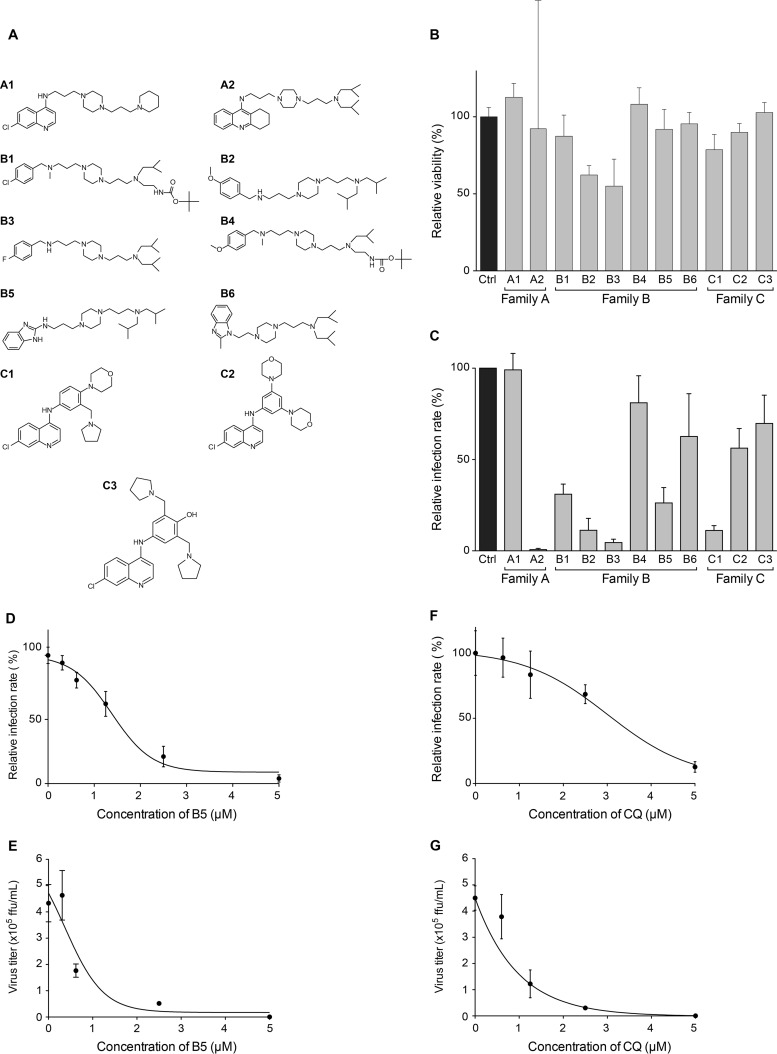
FIG 2.
B5 inhibits HCV infection. (A) Chemical structures of the compounds. (B) B5 toxicity was tested on Huh-7 cells. Cells were cultured in the presence of 5 μM B5, and their viability was monitored using an MTS-based viability assay at 48 h. (C) Anti-HCV activity of the compounds tested at 5 μM, a noncytotoxic concentration. (D to G) Anti-HCV activities of B5 (D and E) and CQ (F and G). Huh-7 cells were pretreated for 1 h with B5 (D and E) or CQ (F and G) before infection with JFH1 (multiplicity of infection [MOI] of 1), and infected cells were in contact with the drugs until the end of the experiment. At 48 h postinfection, infected cells were quantified by indirect immunofluorescence (C, D, and F), and virus released in the supernatant was titrated (E and G). For the infected cells, results are expressed as percentage of infection compared to the control infection in the presence of the solvent. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means (D and F) or standard deviations (SD) (E and G) from at least two independent experiments.