FIG 5.
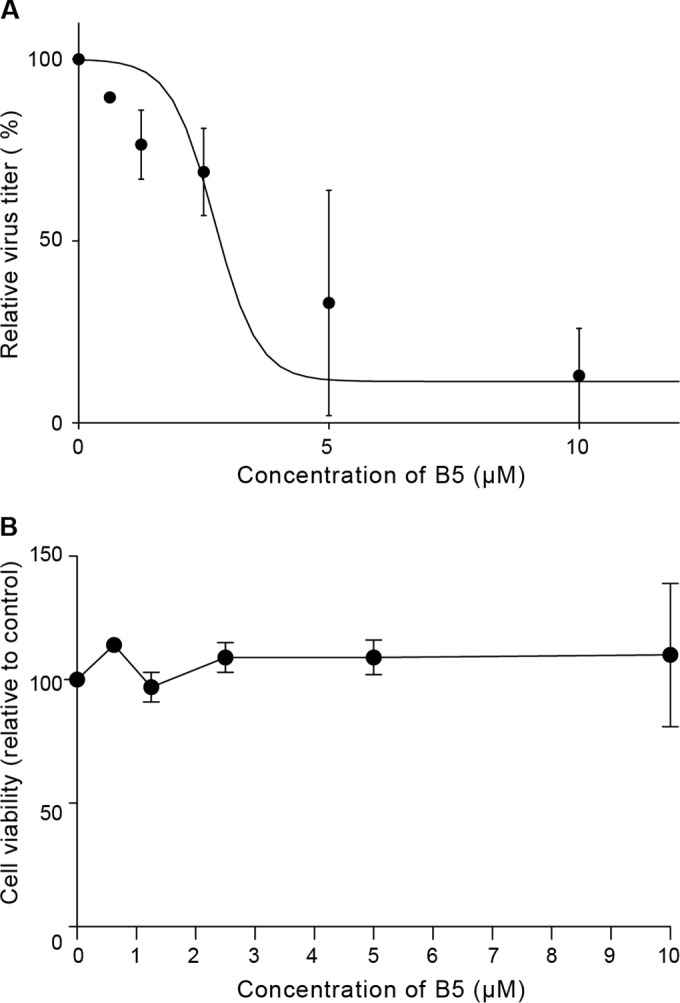
B5 inhibits HCV infection in primary human hepatocytes. (A) Dose-dependent decrease of infectious virus titers released from freshly isolated primary human hepatocytes infected with JFH1 (MOI of 2.5) and treated with increasing amounts of B5 or solvent for 3 days. Shown are infectivity titers (in FFU/ml) expressed as percentage of the solvent control value. Mean values ± SD (error bars) from two different experiments are presented. (B) Toxicity of B5 on primary human hepatocytes. Cells were cultured in the presence of different concentrations of B5, and their viability was monitored after 3 days using CytoTox 96 nonradioactive cytotoxicity assay-based measurement of lactate dehydrogenase leakage by determining optical density at 490 nm. Results are means ± SD (error bars) from at least two experiments.
