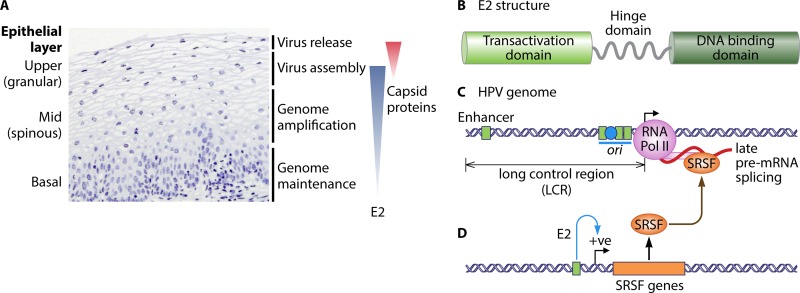
FIG 1.
Activity of E2 during the human papillomavirus (HPV) replication cycle. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin-stained (blue stain) high-risk human papillomavirus (HR-HPV)-positive low-grade cervical lesion. The various epithelial layers are indicated on the left. Note the enlarged nuclei (a hallmark of HPV infection) of cells in the midepithelial layers. The events in the HPV replication cycle and an approximate indication of where they occur within the infected epithelium are indicated on the right. The blue-shaded triangle indicates the extent of E2 expression in the epithelium, and the red-shaded triangle indicates the restricted expression of the viral capsid proteins L1 and L2 in the upper epithelial layers. (B) Diagrammatic representation of the domain structure of E2. Light green, the transactivation domain; dark green, the DNA binding domain; gray wavy line, the hinge domain. (C) A portion of an α-genotype HPV genome is shown from the enhancer in the long control region (LCR) to the late gene region. In the LCR, the four E2 homodimer binding sites are represented by green squares and the E1 binding site is indicated with a blue circle in the origin of DNA replication (ori, blue horizontal line). In mid- to upper epithelial layers, the viral late promoter (black arrow) is active, and the viral late RNAs (shown as a red curved line) are expressed. RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is shown as a pink circle, with an extension indicating the carboxy-terminal domain. SRSF proteins are indicated by an orange oval binding the late pre-mRNA. (D) An E2 binding site (green box) is shown in the promoter of SRSF genes (orange rectangle); E2 (not shown) binds to it to trans-activate (blue curved arrow, positive [+ve]) expression of SRSF genes. A brown curved arrow indicates E2-transactivated SRSF (orange oval)-regulated activity in HPV late mRNA processing (31). However, E2 may also upregulate late mRNA production directly by recruiting other cellular RNA processing factors (39) or by acting as a viral SRSF-like regulator of late mRNA splicing (21).