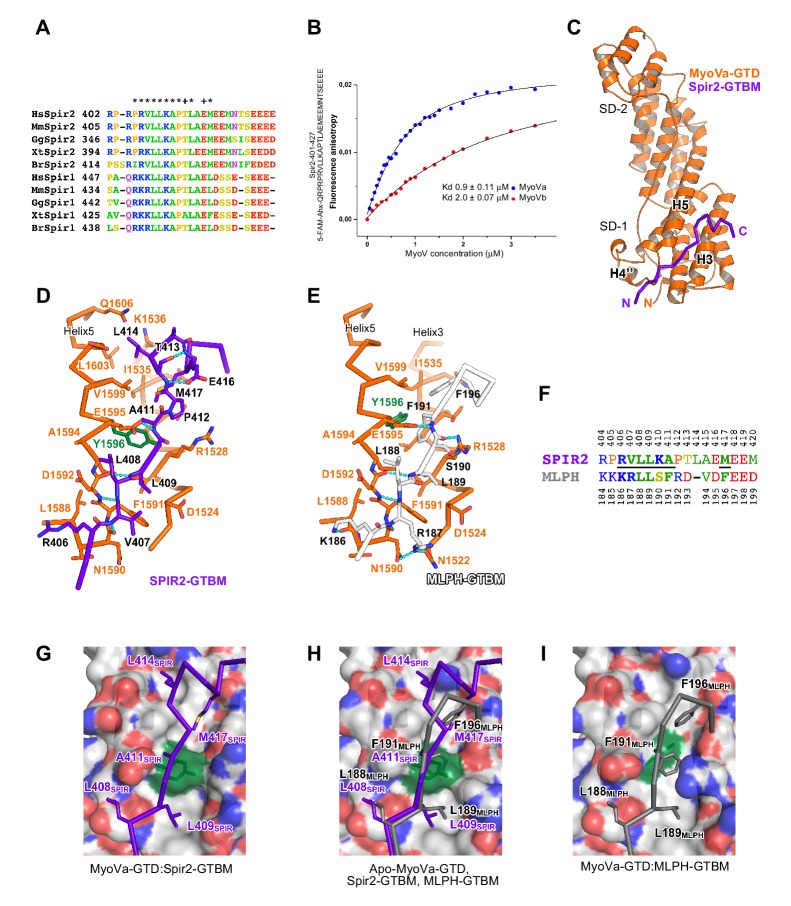
Figure 4. A conserved sequence motif of Spir binds to MyoV-GTD.
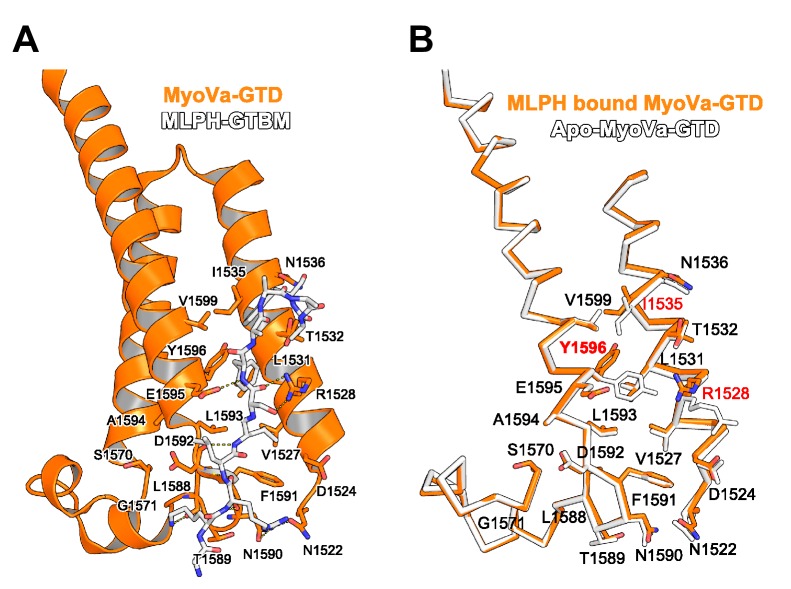
(A) A short highly conserved sequence motif within the central Spir linker region is responsible for myosin V binding. Alignment of vertebrate Spir-1 and Spir-2 sequence fragments. The short sequence motif of about 27 amino acids in the middle part of the Spir linker region shows high sequence homology (see also Figure 4—figure supplement 1). Species abbreviations: Homo sapiens (Hs), Mus musculus (Mm), Gallus gallus (Gg), Xenopus tropicalis (Xt), Brachydanio rerio (Br). All sequence-related data are available through CyMoBase (http://www.cymobase.org). Hs-Spir-2 residues contacting MyoVa within 4 Å distance are labeled with '*'; the Spir-2 conformation is stabilized by two conserved residues (see panel D) indicated with '+'. (B) Fluorescence anisotropy measurements of the binding of the Fluorescein-Spir-2-GTBM peptide (human, amino acid residues 401–427) to the MyoVa and MyoVb GTDs. The equilibrium dissociation constants (Kd) for MyoVa and MyoVb GTDs were determined by fitting the titration curves as detailed in the Materials and Methods section. The experiments were repeated twice with two different protein preparations. (C) Crystal structure of the MyoVa-GTD:Spir-2-GTBM complex. Spir-2-GTBM (purple) binds to subdomain-1 (SD-1) of MyoVa-GTD (orange). (D) Close-up view of the Spir-2-GTBM bound to MyoVa-GTD. Residues forming the interaction sites are shown as sticks and are labeled. Spir-2 E416 and T413 form intramolecular hydrogen bonds (dashed lines). Spir-2 V407, L409 and MyoVa N1590 and D1592 backbone atoms form an intermolecular β-structure like hydrogen bond network. (E) MLPH-GTBM bound to MyoVa-GTD (PDB ID 4LX2). The N-terminal part of MLPH-GTBM (residues from K186 to L189) interacts with MyoVa in a similar manner to Spir-2 (residues 406–409). A similar hydrogen bond between MyoVa E1595 and the main chain nitrogen of MLPH F191 is also observed in the Spir-2:MyoVa interface. (F) Structure based sequence alignment of the Spir-2-GTBM and MLPH-GTBM fragments. Residues making similar contacts with MyoVa are highlighted with a black line. (G) Hydrophobic residues anchoring Spir-2-GTBM on the MyoVa-GTD surface. Spir-2 A411 is packed on the top of MyoVa Y1596 (green) side chain (see also panel D). (H) Spir-2 (purple) and MLPH (gray) GTBMs docked on the surface of apo-MyoVa-GTD (PDB ID 4LX1). The apo-MyoVa-GTD hydrophobic cleft between the H5 and H3 is compatible with Spir-2 binding, but not with MLPH, where the side chain of F191 clashes with MyoVa Y1596 (green). In Spir, the conserved L414 side chain anchors the C-terminal Spir-2 fragment extending the interacting hydrophobic surface compared to what is found for MLPH-GTBM binding. (I) Hydrophobic residues anchoring MLPH-GTBM in the MyoVa-GTD pocket (PDB ID 4LX2). The MyoVa Y1596 (green) side chain is rotated to bury the side chain within the protein core (see also panel E) to accommodate MLPH F191 in the binding pocket.