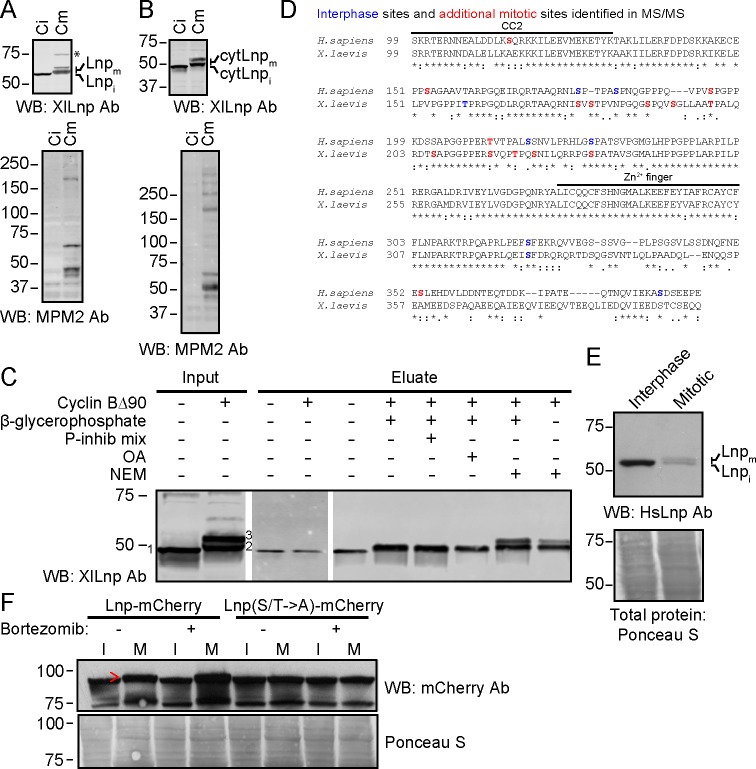
Figure 12. Mitotic phosphorylation of Lnp.
(A) Xenopus egg interphase cytosol, membranes, and an energy regenerating system were incubated with buffer (Ci) or non-degradable cyclin B∆90 (Cm) for 40 min. The samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with Xenopus Lnp antibodies (XlLnp Ab). The lower panel shows an immunoblot with MPM2 antibodies that recognize mitotically phosphorylated proteins. (B) As in (A), but cytLNP was incubated with cytosol in the absence of membranes. (C) Purified HA- and His-tagged cytLnp (HA-cytLnp) was incubated with interphase cytosol with or without cyclin B∆90. An aliquot was analyzed directly by SDS-PAGE (input), while the remainder was incubated with cobalt resin in the presence of various inhibitors (P-inhib is a phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Sigma); OA, okadaic acid; NEM, N-ethylmaleimide). Material eluted from the beads with imidazole (eluate) was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with Xenopus Lnp antibodies. Band 1, unmodified HA-cytLnp; bands 2 and 3, mitotically modified Lnp. (D) Alignment of the cytosolic domains of human and Xenopus LNP sequences. Residues in blue are phosphorylated in interphase, as determined by mass spectrometry. Residues in red are additionally phosphorylated during mitosis. (E) U2OS cells were grown in complete medium and left untreated or treated with 100 nM nocodazole overnight. Interphase cells were scraped off, while mitotically arrested cells were collected as non-adherent cells. Equal amounts of total protein were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies to human Lnp (HsLnp). Lnpi and Lnpm, interphase and mitotic Lnp, respectively. (F) Lnp-mCherry or Lnp-mCherry with Ser and Thr phosphorylation sites mutated to Ala (S/T ->A) were stably expressed in U2OS cells. Cells were arrested in mitosis by incubation with 100 nM nocodazole overnight. Where indicated, 100 nM bortezomib was present overnight. Equal amounts of total protein from interphase (I) or mitotic (M) cells were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with mCherry antibodies. The arrowhead indicates the position of mitotically phosphorylated Lnp.