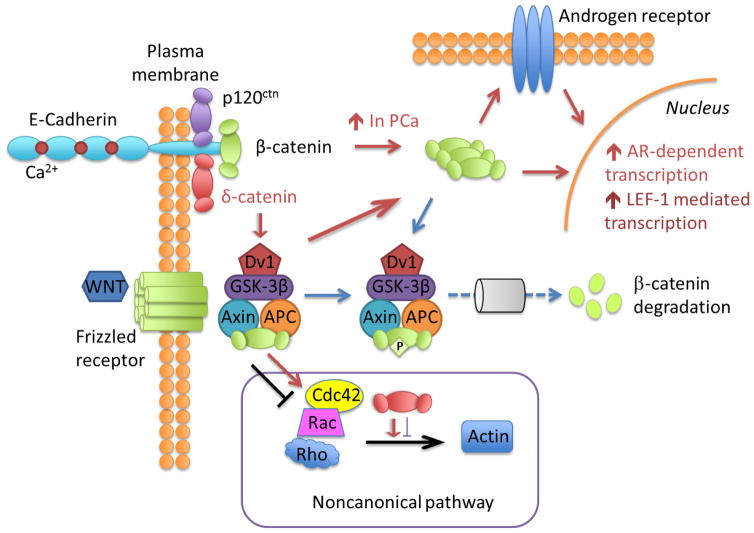
Figure 2. Summary of Wnt signaling involving δ-catenin and Rho GTPases.
The signaling of δ-catenin is highlighted in brown arrows. Overexpression of δ-catenin in prostate cancer (PCa) leads to increased β-catenin levels leading to its translocation to the nucleus to promote LEF-1-mediated and androgen receptor (AR) dependent transcription. Wnt-signaling also leads to β-catenin translocation. Wnt-GSK-dependent proteolysis of β-catenin is highlighted in blue. GSK phosphorylates β-catenin that signals ubiquitination/proteasome degradation. The box highlights the noncanonical/Rho GTPase pathway of δ-catenin involvement in Wnt signaling. Rho GTPases are mediators of Wnt signaling (highlighted in black). δ-Catenin can interrupt Rho GTPase signaling thus affecting actin-mediated dendritic and spine morphogenesis.