Figure 4. A novel mutational hotspot in ARID5B.
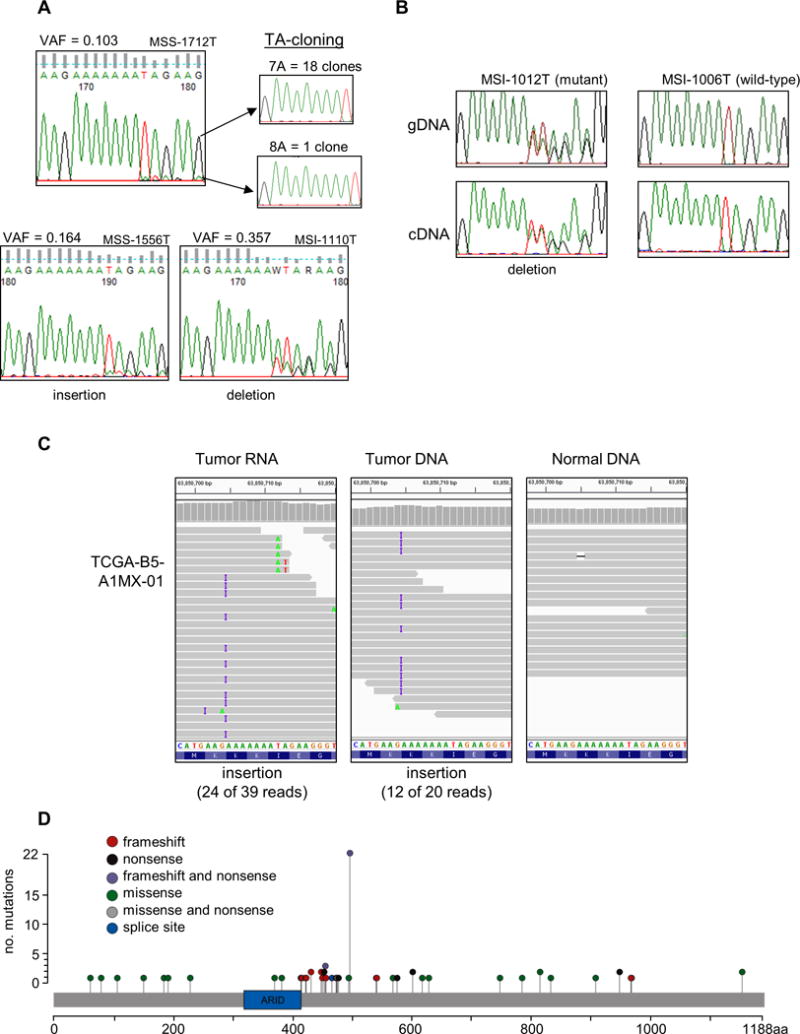
(A) Sanger sequencing chromatograms validate sub-clonal mutations called using MonoSeq. The MonoSeq variant allele fraction (VAF) parallels Sanger sequencing minor peak height. Inserts are chromatograms of cloned and sequenced PCR products from sample MSS-1712T, which confirms the tumor harbors a sub-clonal mutation. (B) Transcripts harboring the frameshift mutation were detectable in cDNA from sample MSI-1012T. Chromatogram for sample MSI-1006T is shown as a representative wild-type. (C) The ARID5B hotspot mutation is in TCGA-B5-A1MX-01. Twenty-four of 39 RNAseq reads displayed the insertion, and 12 of 20 DNA reads had the same mutation. In normal DNA from the same patient, only one of 18 reads displayed an A track mutation, which we attribute to sequencing error. (D) All ARID5B coding exons were sequenced for 540 endometrioid endometrial cancer specimens. Lollipop plot shows 72 mutational events (47 different mutations in 67 samples). Variants were called using VarScan and MonoSeq. ARID domain is represented by green box. Data displayed using Integrated Genomics Viewer software (Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA). All variants detected in this paper were submitted to COSMIC public database (http://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic).
