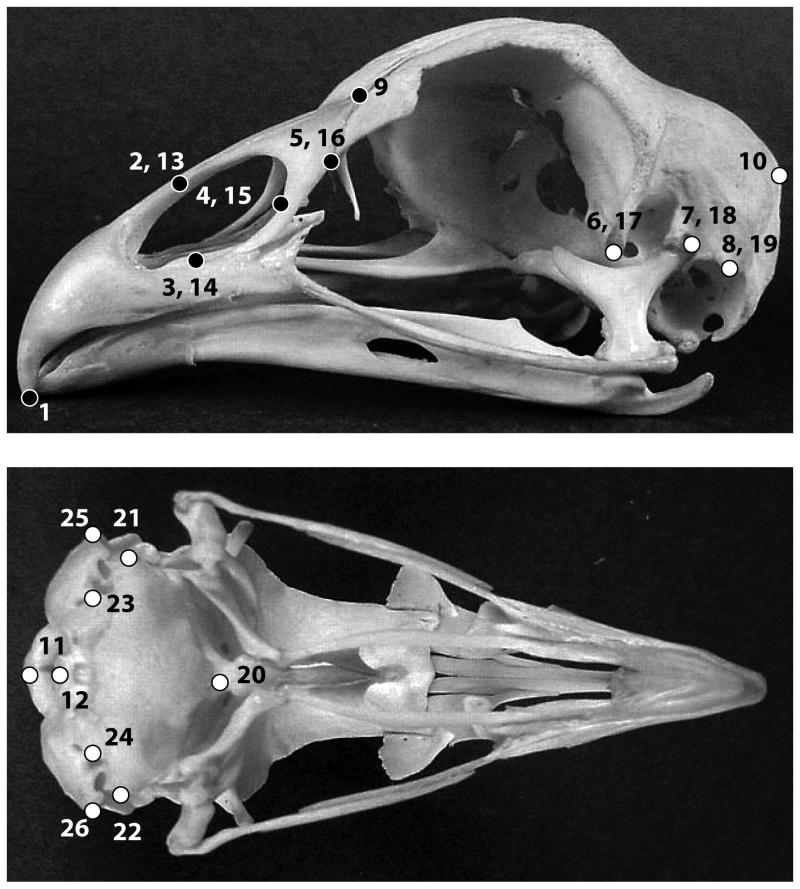
Figure 2.
Localization of landmarks used to describe cranium shape in this study. Black and white dots represent beak and braincase landmarks, respectively (1: tip of the premaxilla; 2, 13: nasal bone – premaxilla juncture [dorsal]; 3, 14: nasal bone – premaxilla juncture [ventral]; 4, 15: posterior-most point of the nasal orifice; 5, 16: anterior-most point of the lacrimal; 6, 17: tip processus postorbitalis; 7, 18: quadrate – cranium joint; 8, 19: tip processus musculi depressor mandibulae; 9: tip processus frontalis premaxillare; 10: anterior-most middle point squamosal-parietal juncture; 11: anterior-most middle point foramen magnum; 12: incisura mediana condyli; 20: bassioccipital process; 21: lateralmost point bassioccipital [right]; 22: lateral-most point bassioccipital [left]; 23: foramen nervi vagi [right]; 24: foramen nervi vagi [left]; 25: tip processus paraoccipitalis [left]; 26: tip processus paraoccipitalis [right]) (Images downloaded from www.skullsite.com).