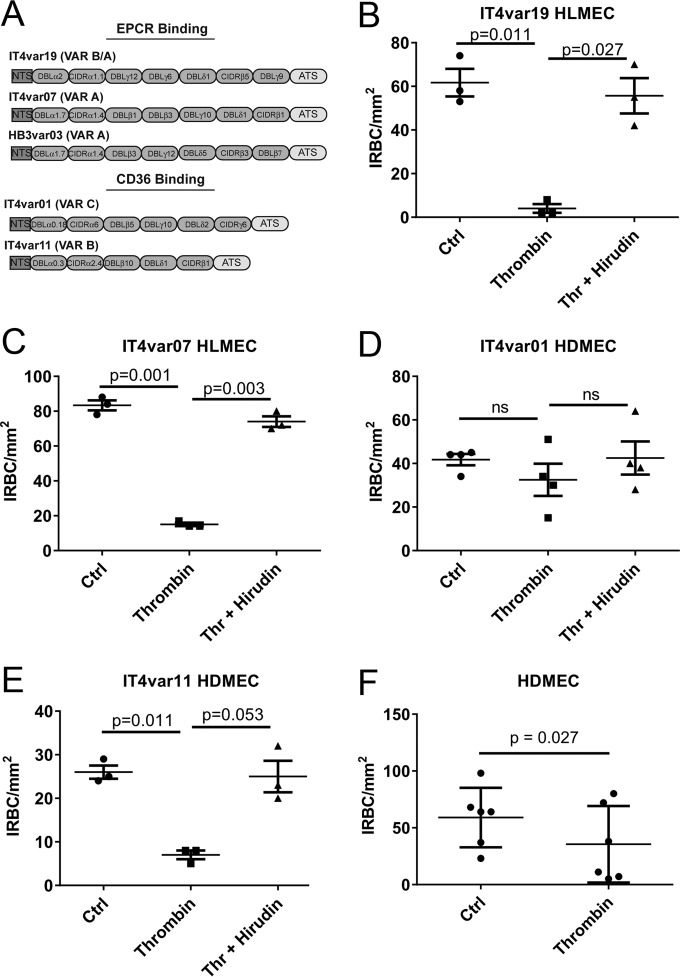
FIG 1 .
Thrombin inhibits adhesion of P. falciparum IRBC with diverse binding phenotypes to microvascular endothelial cells. (A) Schematic of the extracellular domain architecture for the 5 laboratory-adapted P. falciparum parasite lines used in this study. EPCR and CD36 binding parasite lines expressing a predominant var gene were derived from the parental parasite lines FCR3/IT4 and HB3. Each var gene is composed of a cysteine-rich interdomain region (CIDR) and Duffy-binding like (DBL) domains. (B to E) Adhesion of IRBC from IT4-derived parasite lines pretreated with 10 nM thrombin with or without 100 nM hirudin for 30 min at 37°C. Adhesion assays on HLMEC or HDMEC were performed using IRBC at 1% hematocrit and 4 to 5% parasitemia in a parallel-plate flow chamber at 1 dyne/cm2 (n = 3, except for panel E, where n = 4). Ctrl, control. Results are shown as mean ± SEM and were analyzed by ANOVA followed by post hoc multiple comparisons using Tukey’s test. (F) Adhesion of six cryopreserved clinical parasite isolates obtained from infected adult Thai patients on HDMEC. IRBC were pretreated with 25 nM thrombin before being used in the flow chamber assay. Results are shown as mean ± SEM and were analyzed by Student’s paired t test.