FIG 3 .
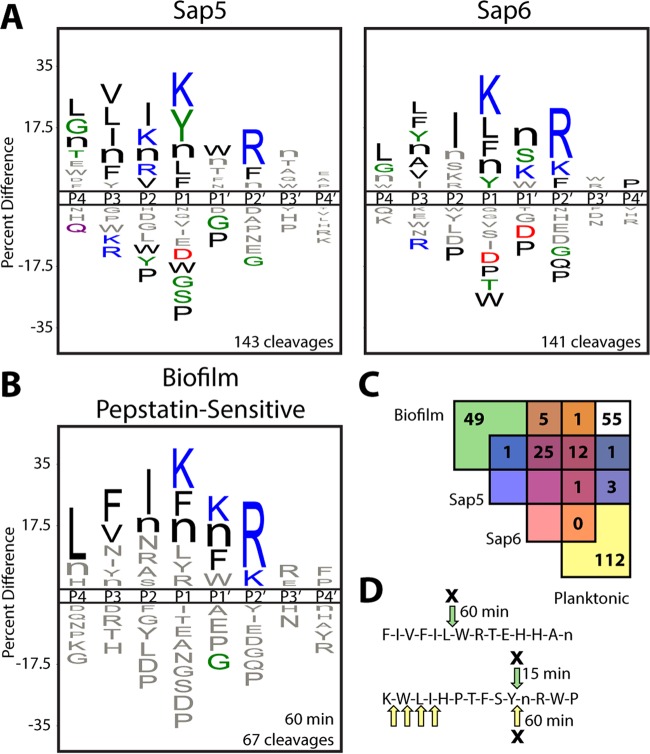
Global protease substrate specificity profiling reveals that Sap5 and Sap6 activities are highly increased in C. albicans under biofilm growth conditions. (A) iceLogo representations of recombinantly produced Sap5 and Sap6 following 240 min of incubation with the MSP-MS peptide library (P ≤ 0.05 for residues colored by physicochemical property). Further comparison of Sap5 and Sap6 specificity is shown in Fig. S4 in the supplemental material. (B) iceLogo representation of cleavages from the C. albicans biofilm conditioned medium MSP-MS assay that are sensitive to pretreatment with the aspartyl protease inhibitor pepstatin A (10 µM). (C) Assignment of pepstatin-sensitive cleavages in the biofilm and planktonic profiles through comparison to recombinantly produced Sap5 and Sap6. The biofilm (60 min) and planktonic (240 min) time points were chosen to normalize for the higher total proteolytic activity under the biofilm condition. iceLogo representations for unassigned cleavages are distinct from the Sap5 and Sap6 specificity profiles and are provided in Fig. S5 in the supplemental material. (D) Example peptide cleavages from the biofilm (green arrows) and planktonic (yellow arrows) MSP-MS assays are shown with pepstatin-sensitive cleavages indicated by an X and the time point of first appearance noted. Selected cleavages were omitted for clarity. All MSP-MS cleavages identified are provided in Data Set S1 in the supplemental material.