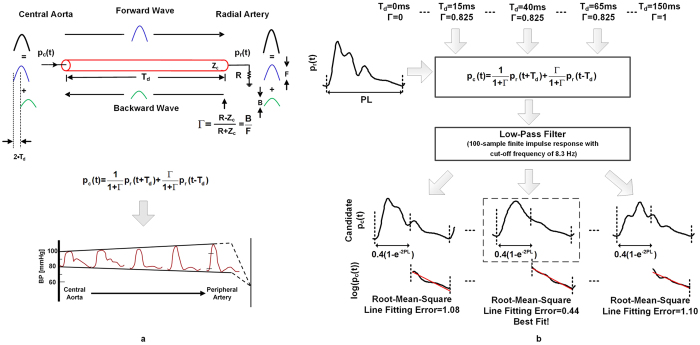
Figure 1. Adaptive transfer function (ATF) for deriving the central blood pressure (BP) waveform from a radial BP waveform.
(a) Tube-load model of arterial wave transmission and reflection upon which the ATF is based (left). The model mimics the progressive amplification as well as distortion that experimental BP waveforms undergo with increasing distance from the heart (bottom) (reproduced after23). According to the model, the transfer function relating radial BP [pr(t)] to central BP [pc(t)] may be defined in terms of two parameters, the wave travel time [Td] and wave reflection coefficient [Γ]. Zc is the arterial characteristic impedance, and R is peripheral resistance. (b) The parameters of the model-based transfer function are determined from only the radial BP waveform by exploiting the frequent observation that central BP waveforms exhibit exponential diastolic decays. In particular, the parameters, and thus the central BP waveform, are estimated so as to make the diastolic intervals of the central BP waveform as exponential as possible in the least squares sense. PL is pulse length.