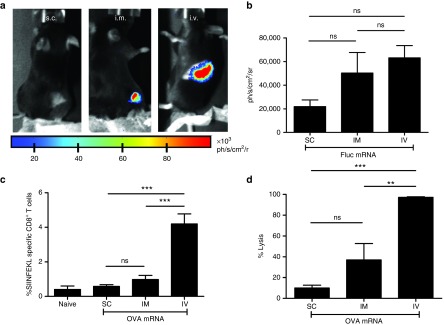
Figure 2.
Intravenous but not s.c. or i.m. delivery of lipid mRNA particles (LMPs) results in potent ovalbumin (OVA)-specific T-cell responses. (a) Representative in vivo bioluminescence images after s.c., i.m., or i.v. delivery of 10 µg Fluc mRNA (n = 4). (b) The graph summarizes the results shown in a as mean ± SEM (n = 4). (c,d) C57BL/6 mice received a s.c., i.m., or i.v. injection with LMPs containing 5 µg OVA mRNA. Five days later, we performed c a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Dextramer staining to detect H-2Kb/SIINFEKL (OVA)-specific T cells and d an in vivo cytotoxicity assay to detect lyses of OVA-presenting target cells (n = 4). SC, subcutaneous; IM, intramuscular; IV, intravenous; ns, not significant.