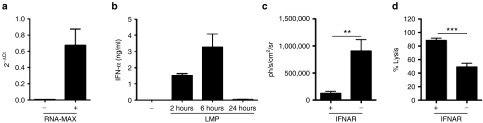
Figure 6.
Type I interferon (IFN) induced by i.v. delivery of lipid mRNA particles (LMPs) enhances antigen-specific immune responses. (a) Mx1 quantitative real-time polymerace chain reaction on mRNA extracted from the spleen 6 hours after i.v. delivery of LMPs. The graph depicts the 2−ΔCt values as mean ± SEM (n = 4). (b) IFN-α ELISA of blood samples collected 2, 6 and 24 hours after i.v. injection of LMPs. The graph depicts the concentration of IFN-α (ng/ml) as mean ± SEM. (c) Wild type or IFNAR−/− mice received an i.v. injection of 10 μg Fluc mRNA. Four hours later, we performed in vivo bioluminescence imaging. The graph depicts the Fluc expression as mean ± SEM (n = 8–10). (d) Wild type or IFNAR−/− mice received an i.v. injection with LMPs containing the 5 µg OVA mRNA. Five days later, we performed the in vivo cytotoxicity assays. The percentage-specific lysis is shown in the graph as mean ± SEM (n = 6–7).