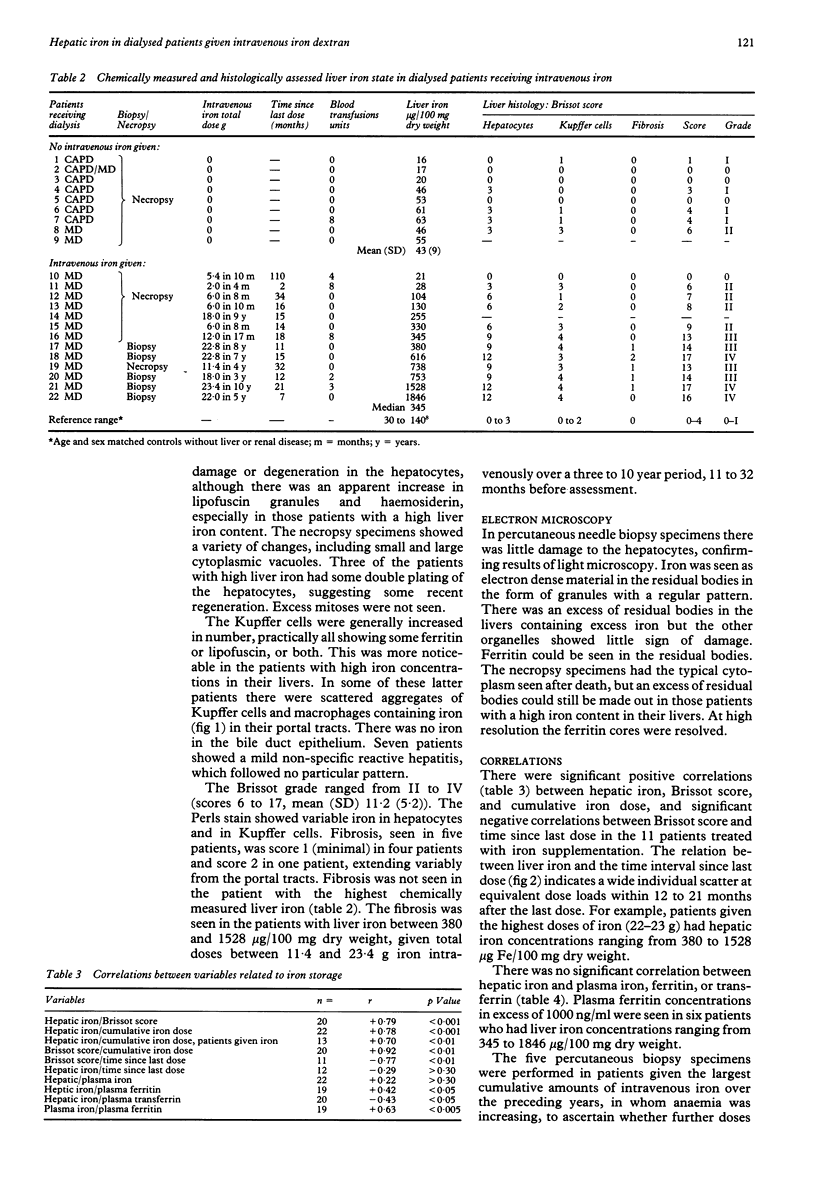
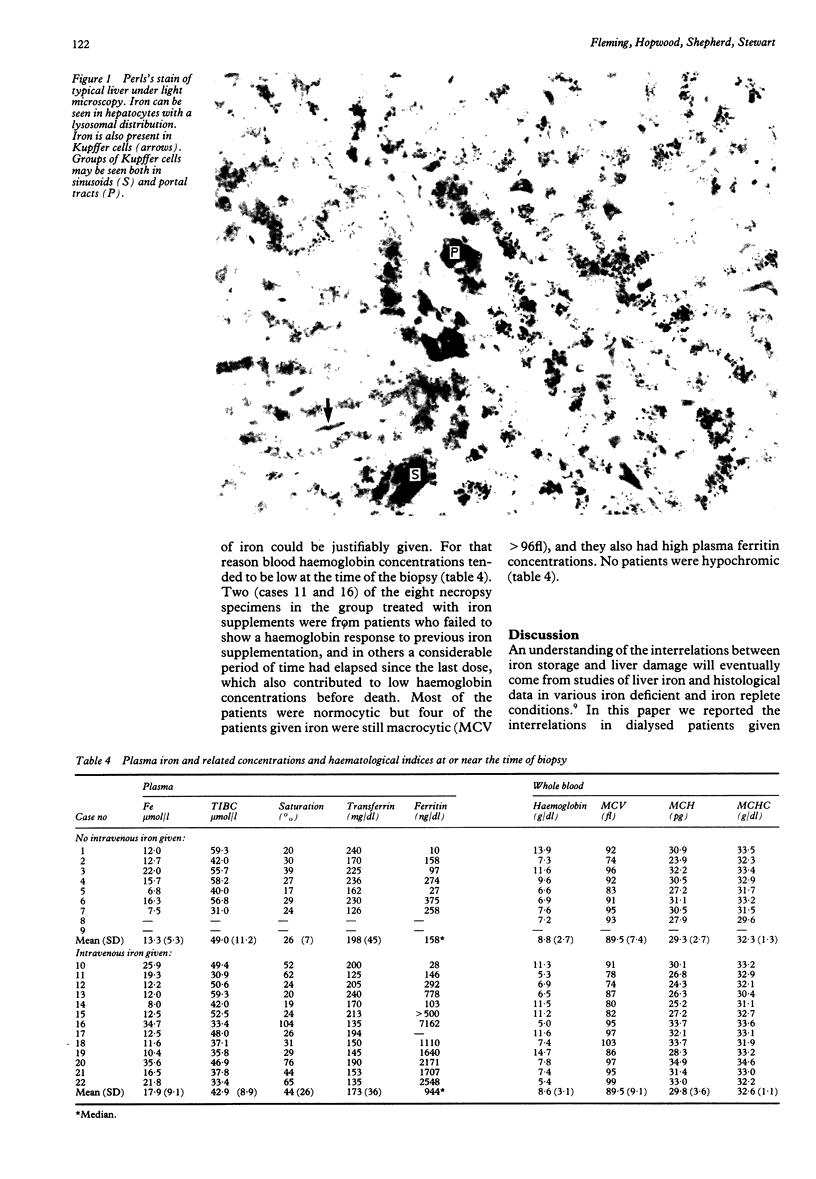
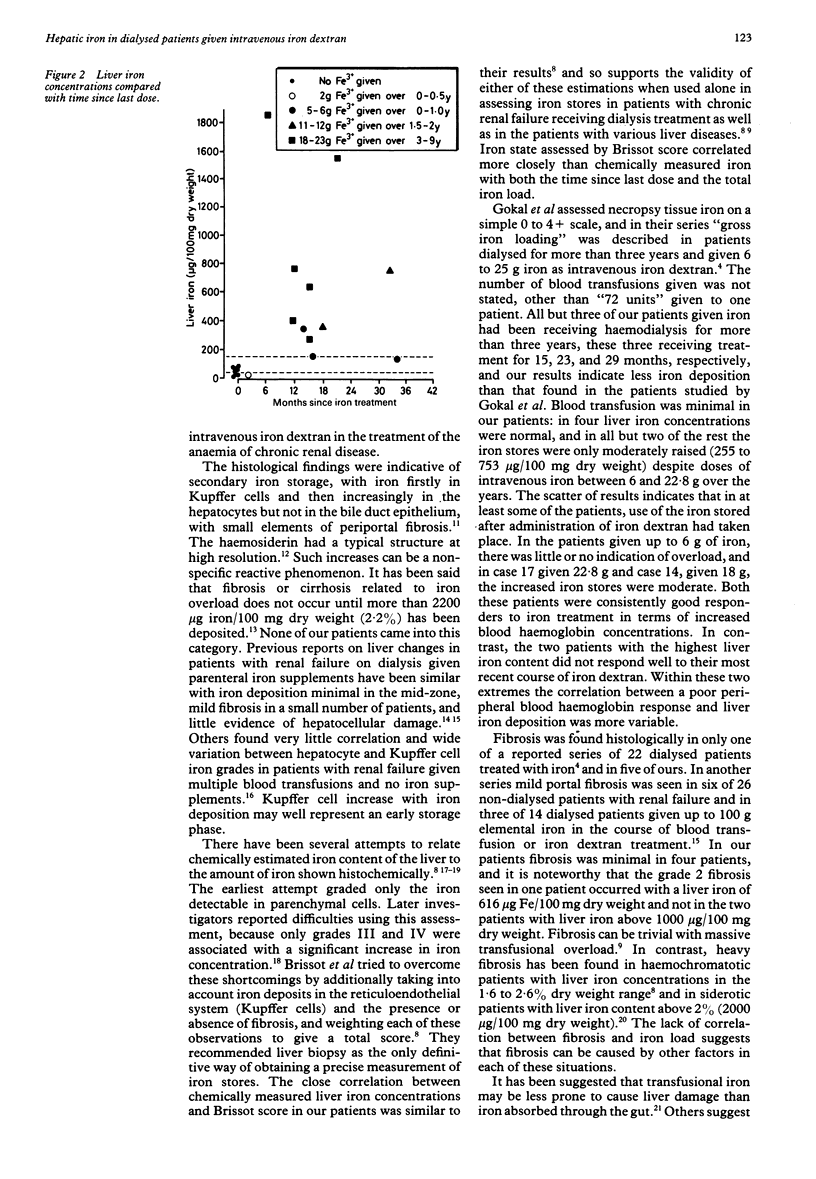
Abstract
Five percutaneous biopsy and 17 necropsy liver specimens were analysed histologically and chemically for iron content in 22 patients receiving dialysis for chronic renal failure, 13 of whom were given intravenous iron-dextran. Brissot scores for assessing histological hepatic iron deposition and chemically measured liver iron concentrations correlated closely. Both variables depended on total cumulative dose of iron, and to a lesser extent, on time since the last dose. Fibrosis (seen in five patients) was minimal and non-specific. Electron microscopic examination showed that there was no generalised damage and confirmed the presence of iron in the hepatocytes in the form of ferritin. High liver iron concentrations, in excess of 1000 micrograms/100 mg dry weight, were seen in two patients. Four others given comparable cumulated amounts (18-23 g iron) did not have such high concentrations. Plasma ferritin concentrations were high in eight patients, some with and some without fibrosis. The risk of temporarily high iron deposition in the liver causing damage seemed to be minimal when weighed against the benefit of increased haemoglobin in most of the patients. Intravenous iron treatment merits further evaluation, particularly with the advent of erythropoietin treatment, which requires continuously available iron.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali M., Fayemi A. O., Rigolosi R., Frascino J., Marsden T., Malcolm D. Hemosiderosis in hemodialysis patients. An autopsy study of 50 cases. JAMA. 1980 Jul 25;244(4):343–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali M., Rigolosi R., Fayemi A. O., Braun E. V., Frascino J., Singer R. Failure of serum ferritin levels to predict bone-marrow iron content after intravenous iron-dextran therapy. Lancet. 1982 Mar 20;1(8273):652–655. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOTHWELL T. H., ISAACSON C. Siderosis in the bantu. A comparison of incidence in males and females. Br Med J. 1962 Feb 24;1(5277):522–524. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5277.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry M. Liver iron concentration, stainable iron, and total body storage iron. Gut. 1974 May;15(5):411–415. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.5.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry M., Sherlock S. Measurement of liver-iron concentration in needle-biopsy specimens. Lancet. 1971 Jan 16;1(7690):100–103. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90838-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett M. L., Halliday J. W., Powell L. W. Value of hepatic iron measurements in early hemochromatosis and determination of the critical iron level associated with fibrosis. Hepatology. 1986 Jan-Feb;6(1):24–29. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissot P., Bourel M., Herry D., Verger J. P., Messner M., Beaumont C., Regnouard F., Ferrand B., Simon M. Assessment of liver iron content in 271 patients: a reevaluation of direct and indirect methods. Gastroenterology. 1981 Mar;80(3):557–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming L. W., Saleem A. K., Goodall H. B., Stewart W. K. Bone marrow iron and plasma ferritin in dialysed patients given intravenous iron-dextran. Clin Lab Haematol. 1984;6(1):23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2257.1984.tb00522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei U., Wilks M. F., Boehmer S., Crisp-Lindgren N., Schwarzrock R., Stiekema J. C., Koch K. M. Gastrointestinal blood loss in haemodialysis patients during use of a low-molecular-weight heparinoid anticoagulant. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1988;3(4):435–439. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.ndt.a091694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gokal R., Millard P. R., Weatherall D. J., Callender S. T., Ledingham J. G., Oliver D. O. Iron metabolism in haemodialysis patients. A study of the management of iron therapy and overload. Q J Med. 1979 Jul;48(191):369–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gokal R., Weatherall D. J., Bunch C. Iron induced increase in red cell size in haemodialysis patients. Q J Med. 1979 Jul;48(191):393–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kothari T., Swamy A. P., Lee J. C., Mangla J. C., Cestero R. V. Hepatic hemosiderosis in maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) patients. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 May;25(5):363–368. doi: 10.1007/BF01308060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdougall I. C., Hutton R. D., Cavill I., Coles G. A., Williams J. D. Poor response to treatment of renal anaemia with erythropoietin corrected by iron given intravenously. BMJ. 1989 Jul 15;299(6692):157–158. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6692.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher E. R., Curtis J. R. Serum ferritin in haemodialysis patients: is there a relationship to 'haemochromatosis alleles' HLA A3, B7, B14? Nephron. 1986;43(1):43–44. doi: 10.1159/000183716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. A., Slater D. N., Parsons M. A., Fox M., Smith S., Platts M. M. Splenic siderosis and parenteral iron dextran in maintenance haemodialysis patients. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jan;37(1):59–64. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risdon R. A., Barry M., Flynn D. M. Transfusional iron overload: the relationship between tissue iron concentration and hepatic fibrosis in thalassaemia. J Pathol. 1975 Jun;116(2):83–95. doi: 10.1002/path.1711160204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEUER P. J., WILLIAMS R., MUIR A. R. Hepatic pathology in relatives of patients with haemochromatosis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1962 Jul;84:53–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer A. I., Cheron R. G., Dluhy R., Cooper B., Gleason R. E., Soeldner J. S., Bunn H. F. Clinical consequences of acquired transfusional iron overload in adults. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 5;304(6):319–324. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102053040603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serum ferritin concentrations after intravenous iron-dextran. Lancet. 1982 May 1;1(8279):1017–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valberg L. S., Ghent C. N., Lloyd D. A., Frei J. V., Chamberlain M. J. Diagnostic efficacy of tests for the detection of iron overload in chronic liver disease. Can Med Assoc J. 1978 Aug 12;119(3):229–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Vyver F. L., Vanheule A. O., Verbueken A. H., D'Haese P., Visser W. J., Bekaert A. B., Van Grieken R. E., Buyssens N., De Keersmaecker W., Van den Bogaert W. Patterns of iron storage in patients with severe renal failure. Contrib Nephrol. 1984;38:153–166. doi: 10.1159/000408081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. J., Miller J. P., Dymock I. W., Shilkin K. B., Williams R. Relationship of hepatic iron concentration to histochemical grading and to total chelatable body iron in conditions associated with iron overload. Gut. 1971 Dec;12(12):1011–1014. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.12.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir M. P., Sharp G. A., Peters T. J. Electron microscopic studies of human haemosiderin and ferritin. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Aug;38(8):915–918. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.8.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



