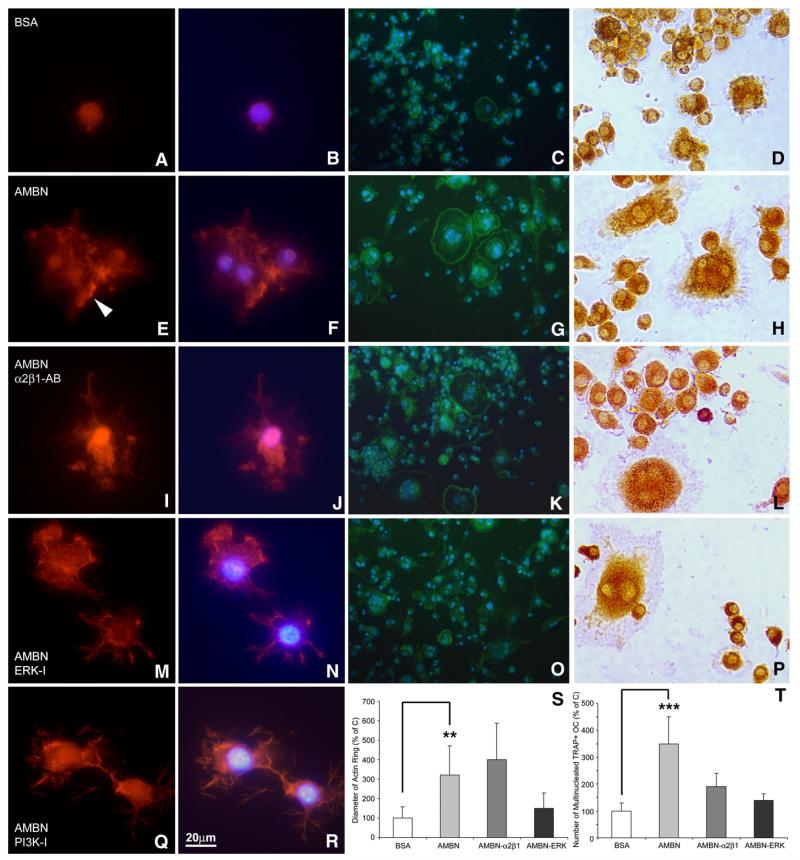
Fig. 7.
Involvement of α2β1 integrins and ERK1/2 in AMBN-modulated formation of podosome and actin ring. (A, B, E, F, I, J, M, N, Q, R) Fluorescent images of BMMCs cultured on dishes treated with either BSA (A and B), AMBN (E and F), AMBN plus α2β1 integrin antibody (I and J), AMBN plus ERK inhibitor (M and N), or AMBN plus PI3K inhibitor (Q and R). Cells were stained with the actin-filament stain rhodamine-phalloidin (A, E, I, M, Q) and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (B, F, J, N, R). Following AMBN treatment, BMMCs displayed podosome-like structures (arrowhead). (C, G, K, O) FITC-phalloidin staining indicated actin ring formation characteristic of osteoclasts. Multiple nuclei were visualized in osteoclasts with actin rings using DAPI (D, H, L, P), TRAP staining showed a pink cytoplasm in multinucleated cells, indicative of mature osteoclasts. (S and T) Comparison of actin ring diameter and TRAP-positive/multinucleated cell density between treatment groups. Data are presented as mean±SD for four different cultures. **=p<0.001, ***=p<0.0001.