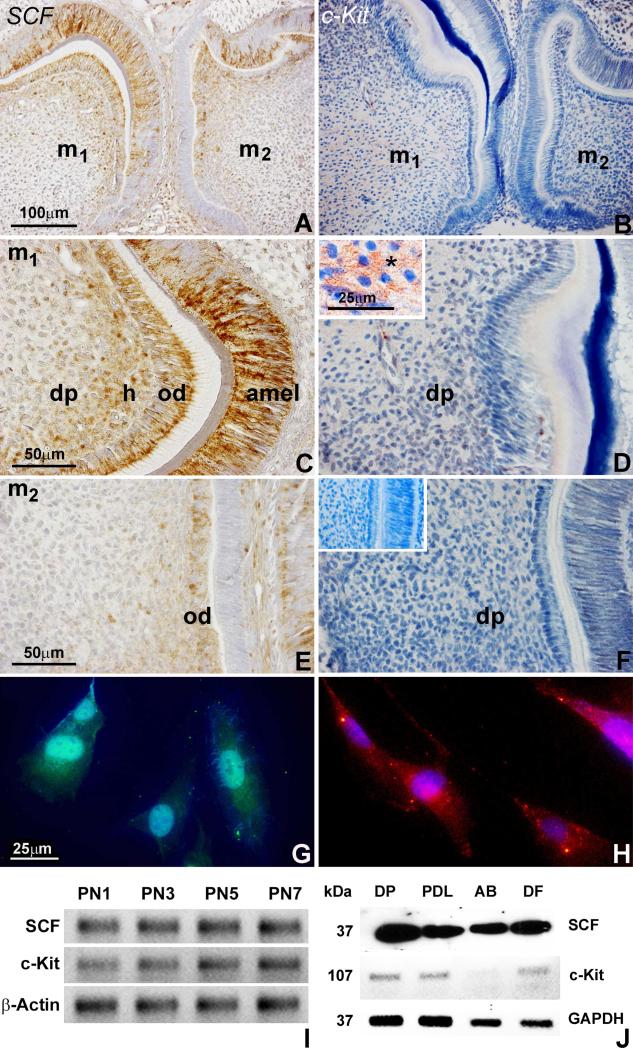
Figure 1. SCF/c-Kit expression and localization during mouse dentinogenesis and in dental pulp progenitors.
(A-F) Immunostained sections of first and second molars from 3 day postnatal mice demonstrating SCF and c-Kit protein localization in the dental pulp (dp), odontoblasts (ob), and ameloblasts (amel). The SCF protein was highly expressed and specifically localized in odontoblasts, Höhl's subodontoblastic layer (h), and adjacent dental pulp of first and second molars (A,C,E). SCF was also detected in secretory ameloblasts (amel)(C). In contrast, the c-Kit protein was evenly distributed in the first molar dental pulp (B,D), and only detected at low levels in the pulp of the second molar (F). The insert (D) illustrates the c-Kit protein network on the surface of dental pulp cells. The second insert (F) is a matching micrograph of an immunostaining control reaction. (G,H) Immunofluorescent analysis of SCF (G) and c-Kit (H) protein localization in dental pulp progenitors. (I) RT-PCR analysis of SCF and c-Kit mRNA expression in the dental papilla from 1, 3, 5, and 7 days postnatal mice. The β-Actin gene was used as internal control. (J) Western blot analysis of SCF and c-Kit protein expression in the dental pulp (DP), periodontal ligament (PDL), alveolar osteoblast (AB) and dental follicle (DF) progenitors. Cell extracts were processed for immunoblotting with antibodies against SCF and c-Kit. GAPDH was detected as a loading control. Note that SCF protein expression was highest in dental pulp and lowest in alveolar osteoblast cells.